Fletikumab Overview
Introduction of Fletikumab and IL20
Fletikumab is a human IgG4-kappa recombinant antibody that targets interleukin-20 (IL-20), an inflammatory cytokine of the IL-10 superfamily. IL-20 is well-known for its involvement in many inflammatory processes, and for contributing to the development of chronic conditions like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), spondyloarthritis (SpA), and other immune disorders.
IL-20 in Inflammatory Diseases
IL-20 for Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis
In RA and SpA, IL-20 has been implicated in bone degeneration and inflammatory signaling. The cytokine's interactions with synovial fibroblasts and macrophages also drive the production of chemokines, such as IL-6 and IL-8. In addition, IL-20 leads to bone erosion by recruiting osteoclast precursors to inflammatory locations, accelerating joint damage.
In trials of fletikumab for RA, it was shown to be safe and effective at reducing disease activity in patients with the infection. However, later-stage trials suggested the need for more combination therapies due to cytokine family redundancy and highlighted the potential for combinatory or receptor-targeting methods.
IL-20 in Acute Kidney Injury and Chronic Kidney Disease
IL-20 has also been implicated in kidney disease, which induces tubular epithelial cell death and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. It turns out that in models of acute kidney injury (AKI) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), IL-20 increases pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TGF-1 and MCP-1, thereby accelerating kidney inflammation and fibrosis. Fletikumab might be therapeutically beneficial by inhibiting these damaging processes. Hypoxia induced by many acute diseases such as ischemic kidney injury can stimulate the expression of IL-20. In these conditions, interrupting IL-20 helps to inhibit both inflammatory cell proliferation and fibrosis, underscoring the therapeutic promise of IL-20 inhibitors in hypoxic disorders.
Biological and Chemical Properties of IL20
Protein Structure
 Figure 1. The Structure of Human IL20 (UniProt)1,2.
Figure 1. The Structure of Human IL20 (UniProt)1,2.
The Mechanism of Fletikumab Action
IL-20 signals mainly via the Janus kinase (JAK)-STAT pathway by interacting with its receptor complexes, IL-20RA/IL-20RB or IL-22RA1/IL-20RB. This signaling drives STAT3 and downstream regulators such as Akt and ERK, leading to inflammation, fibrosis, and tissue remodeling.
Fletikumab targets IL-20 by inhibiting its primary binding to receptors. This neutralization stops the pro-inflammatory cascade, preventing cytokine-induced cellular activity. By acting on IL-20, fletikumab provides a targeted way to regulate inflammatory mechanisms, which may reduce the adverse effects of general immunosuppressive drugs. IL-20 is abundant in the synovial tissues and fluids of RA, which stimulates the production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) and other inflammatory mediators. Fletikumab blocks IL-20, which limits MCP-1 activity, suppresses osteoclastogenesis, and slows the progression of joint damage.
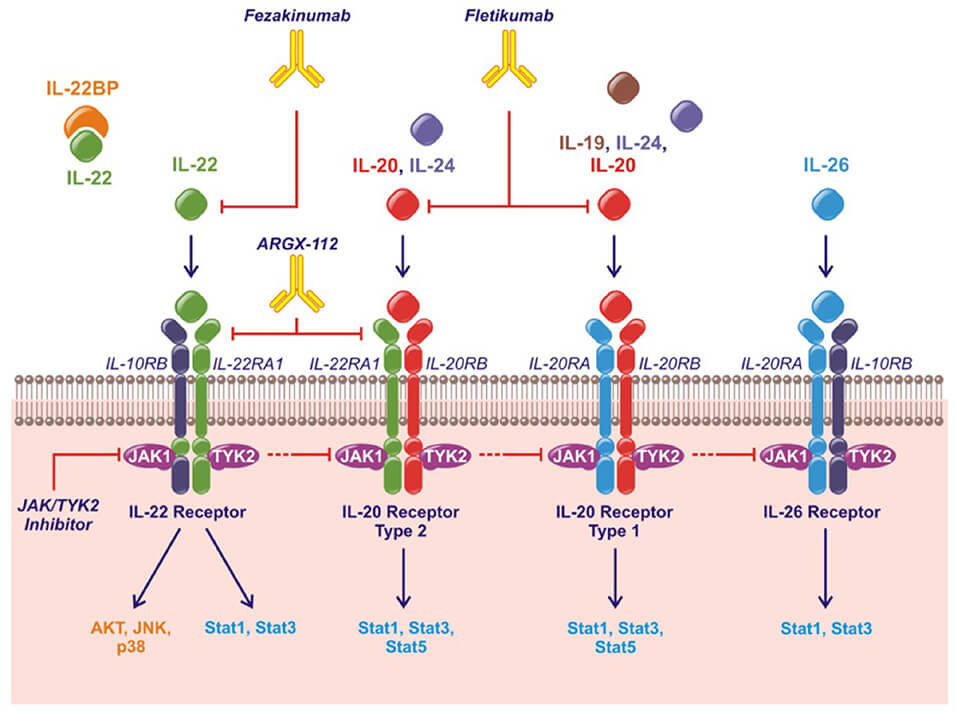 Figure 2. The IL-20 Family of Cytokines, Their Shared Receptors and Intracellular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies3.
Figure 2. The IL-20 Family of Cytokines, Their Shared Receptors and Intracellular Signaling Pathways and Therapeutic Strategies3.
The Clinical Applications of Fletikumab
Fletikumab, as an IL-20-neutralizing antibody, has demonstrated potential in several inflammatory and fibrotic diseases. Its applications highlight the promise of targeted immunotherapy in addressing cytokine-driven conditions.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) and Spondyloarthritis (SpA)
Fletikumab has shown effectiveness in early trials by reducing inflammation and joint damage in RA. It also holds promise in SpA, targeting IL-20-driven inflammation and bone remodeling. However, challenges like cytokine redundancy suggest potential benefits from combination therapies.
Psoriasis
IL-20 drives keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis. While early studies showed limited efficacy, fletikumab remains a candidate for refractory cases, especially when combined with other biologics.
Kidney Diseases (CKD and AKI)
Fletikumab has demonstrated preclinical efficacy in reducing renal inflammation, fibrosis, and cell death. By inhibiting TGF-β1 and MCP-1 pathways, it may help manage CKD and AKI, preserving kidney function.
Emerging Indications
Fletikumab's role extends to liver fibrosis and diabetic nephropathy, where IL-20 contributes to fibrosis, oxidative stress, and inflammation. Blocking IL-20 shows the potential to mitigate progression in these conditions.
What We Provide
Anti-Human IL20 Recombinant Antibody (Fletikumab)
We provide high-quality fletikumab for use in IF, IP, Neut, FuncS, ELISA, FC, ICC, and most other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Host Species
- human
- Derivation
- human
- Type
- IgG4 - kappa
- Specificity
- IL20 (interleukin 20, IL-20) [Homo sapiens]
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in IF, IP, Neut, FuncS, ELISA, FC, ICC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 1357158-22-5
- Generic Name
- fletikumab
- ChEMBL
- CHEMBL3301580
- MW
- 146.5 kDa
- Related Disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- UniProt Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q9NYY1/entry)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0] without modification.
- Kragstrup, Tue W., et al. "The IL-20 cytokine family in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis." Frontiers in immunology 9 (2018): 2226. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

