Seribantumab Overview
Introduction of Seribantumab
Seribantumab (MM-121) is a humanized immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2) monoclonal antibody and has been investigated in various tumor therapies. It is designed to target receptor tyrosine-protein kinase ERBB3, which is also known as human epidermal growth factor receptor 3 (HER3) and is the most critical activator in phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and Protein Kinase B (Akt) signal transduction. This drug was designed to be investigated in the treatment of diseases including Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Heregulin, Adenocarcinoma, Colorectal and Solid cancers.
Mechanism of Action of Seribantumab
ERBB3, a member of the epidermal growth factor kinase family (EGF family), is often overexpressed in solid tumors like lung cancer. The widespread receptors of ERBB3 are signaling molecules that involve in complex signaling pathways, including Ras/Raf/MAPK, PI3K/AKT, Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK/STAT) and PKC (Protein kinase C). Upon ERBB3 binding to its receptors, a drug resistant signaling pathway are activated for cancer cells, allowing them to evade capture form the action of some drugs. Both human clinical and biological cytology studies have shown the potential therapeutic value of ERBB3 in three different cancers (lung, breast and ovarian) that express heregulin. Thus, Merrimack develops seribantumab for cancer treatment designed to the key points in the signaling network of drug resistant pathway induced by ERBB3. Seribantumab is an effective engineered monoclonal antibody designed to block the heregilin/ERBB3 signaling axis via blocking the binding of ERBB3 and its receptor, heregulin. Heregulin is the major class of soluble ERBB3 ligands playing an important role in ERBB3 activation and signaling. About 30%–50% of solid tumor patients with high expression level of heregulin, depending on the cancer type. Heregulin positive cancer cells are characterized by their ability to evade the effects of targeting, cytotoxicity and anti-endocrine therapy. Heregulin is a soluble secreted growth factor that activates ERBB3 and HER4 transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinases and is associated with cell proliferation, invasion, and survival. Seribantumab, when used in combination with other drugs, can block heregulin/ERBB3 signal transduction to make these cells more sensitive to the effects of combination therapy and ultimately improve clinical outcomes. Seribantumab binds to ERBB3 and blocks the signal transduction induced by the extracellular growth factor heregulin.
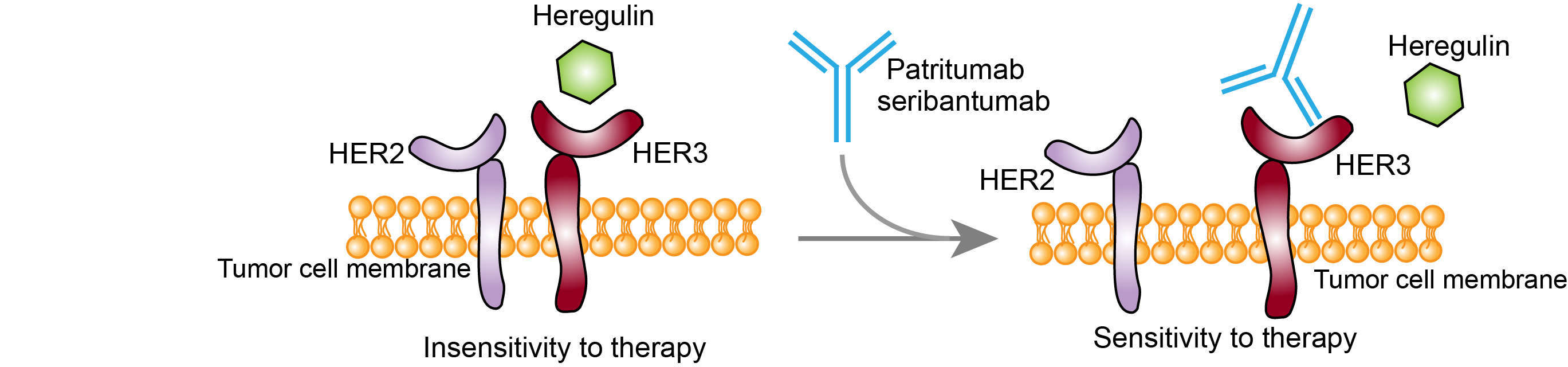 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Seribantumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Seribantumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

