Sirukumab Overview
Introduction of Sirukumab
Sirukumab (developmental code name CNTO-136) is a human monoclonal antibody (mAb) designed for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). It acts against the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL) -6 (IL-6). Sirukumab was evaluated in five Phase 3 studies of patients with RA.
Mechanism of Action of Sirukumab
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune inflammatory disease of the intra-articular synovial tissue. Studies to uncover the cause of RA have ended up scrutinizing the importance of proinflammatory cytokine such as tumor necrosis factor a (TNF-a) and IL-6 in the pathogenesis of RA. IL-6 is a pro-inflammatory cytokine with pleiotropic biological activities. The signaling pathway of IL-6 includes two molecules, a specific receptor for IL-6 and a cell-surface glycoprotein called gp130 as a signal transducer. IL-6 transmits its signal through binding to membrane-bound IL-6R (mIL-6R) or soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) that are respectively called classic signaling and trans-signaling. Binding of IL-6 to mIL-6R or sIL-6R recruits two molecules of ubiquitously expressed gp130 and induces their homodimerization. The formation of functional receptor complex of IL-6, IL-6R, and gp130 subsequently triggers downstream signaling pathway via Janus kinase (JAK) leading to the regulation of transcription factors including STAT3 in target cells. The sIL-6R generated by limited proteolysis of mIL-6R or alternative splicing plays an important role especially in the cells which do not express mIL-6R. In the serum of RA patients, elevated levels of IL-6 and sIL-6R are detected with positive correlation to RA disease severity and radiological joint damage. Moreover, overproduction of IL-6 has been found in the synovial cell and macrophage of the joint of RA patients. IL-6 contributes to induction and maintenance of autoimmune process through B cell modulation and Th17 cell differentiation. IL-6 also plays a role in angiogenesis by inducing intracellular adhesion molecules. These functions of IL-6 in the pathogenesis of RA make IL-6 as a remarkable target for the RA therapy. Sirukumab binds IL-6 with high affinity and specificity, thereby inhibiting IL-6-mediated effects.
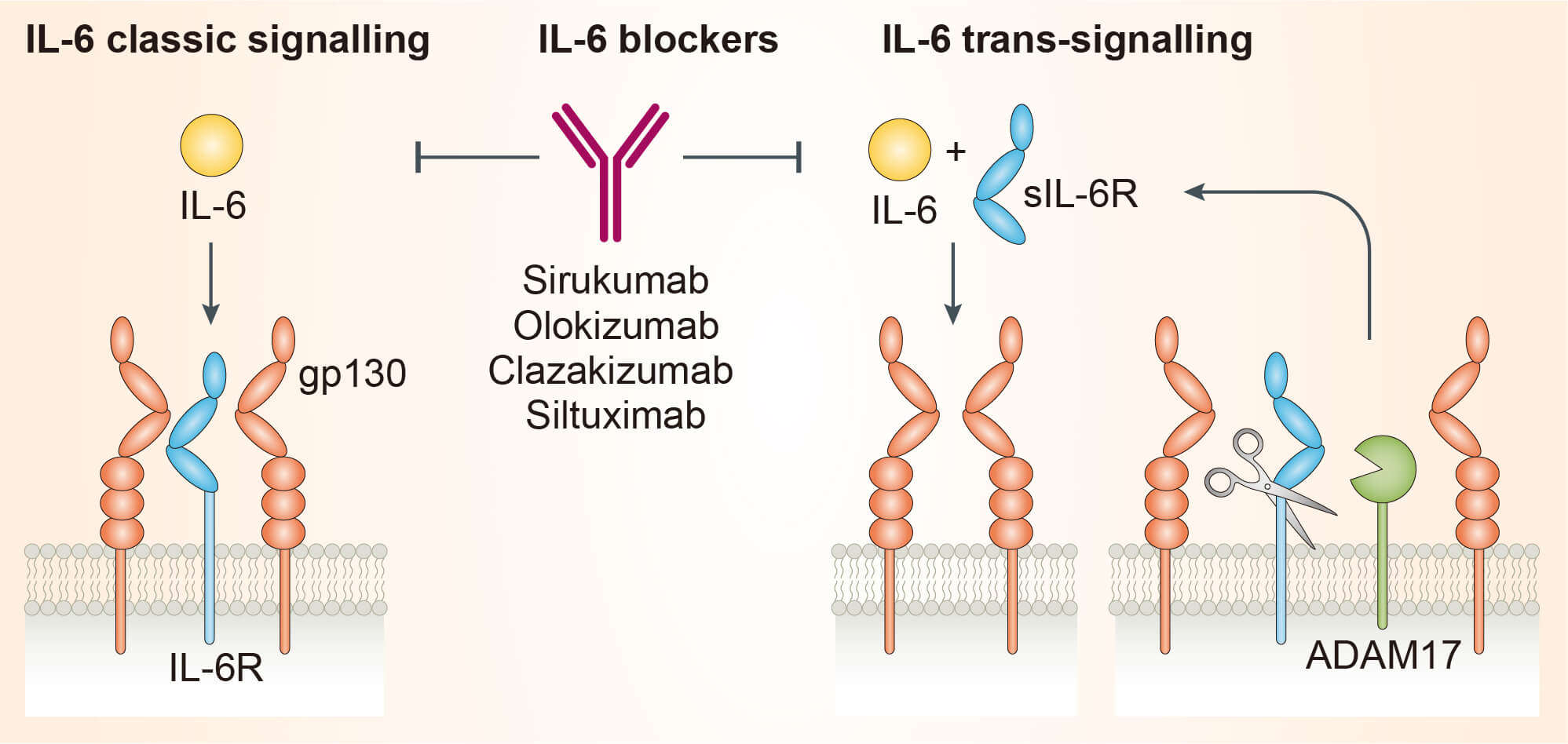 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of sirukumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of sirukumab
Clinical Projects of Sirukumab*
| NCT ID | Status | Conditions | Lead Sponsor | Update Time |
| NCT01856309 | Active, not recruiting | Arthritis, Rheumatoid | Janssen Research & Development, LLC | May 17, 2013 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=&term=Sirukumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

