Telimomab Overview
Introduction of Telimomab
Telimomab marks a new advance in the developing field of targeted immunotherapy. Telimomab is a novel monoclonal antibody that targets CD5, a surface protein expressed on T-cells and some hematopoietic cells. The distinctive mode of action has attracted much attention, in autoimmune and T-cell diseases in particular. Telimomab acts by inhibiting T-cell activation, activating T-cell depletion, and modifying immune tolerance, making it a promising therapy for autoimmune diseases, cancer immunotherapy, and organ transplantation. When it is better understood for its clinical uses, Telimomab could revolutionize our management of immune disorders to allow for more precise and efficient treatments.
Introduction of CD5
Recognizing CD5 and Its Function in Immune Control
CD5 is a glycoprotein expressed on the surface of T-cells and certain B-cells that are crucial to immune control. It is a co-receptor of the T-cell receptor (TCR) and plays a role in controlling the activation, survival, and differentiation of T-cells. The CD5 functions as a dual immune tolerance and immune activation agent, depending on the signal it is sending. In normal circumstances, CD5 is crucial to a healthy immune system in which T-cells are not too reactive to self-antigens, avoiding autoimmunity. But in some pathologies, including autoimmune and chronic inflammatory diseases, CD5's regulatory roles can be lost. Such dysregulation usually leads to hyper-activation of T-cells and worsened immune response. Specifically, Telimomab (targeting CD5) can control this pathway and restore immune system stability, making it a promising therapy for many immune disorders.
Protein Structure
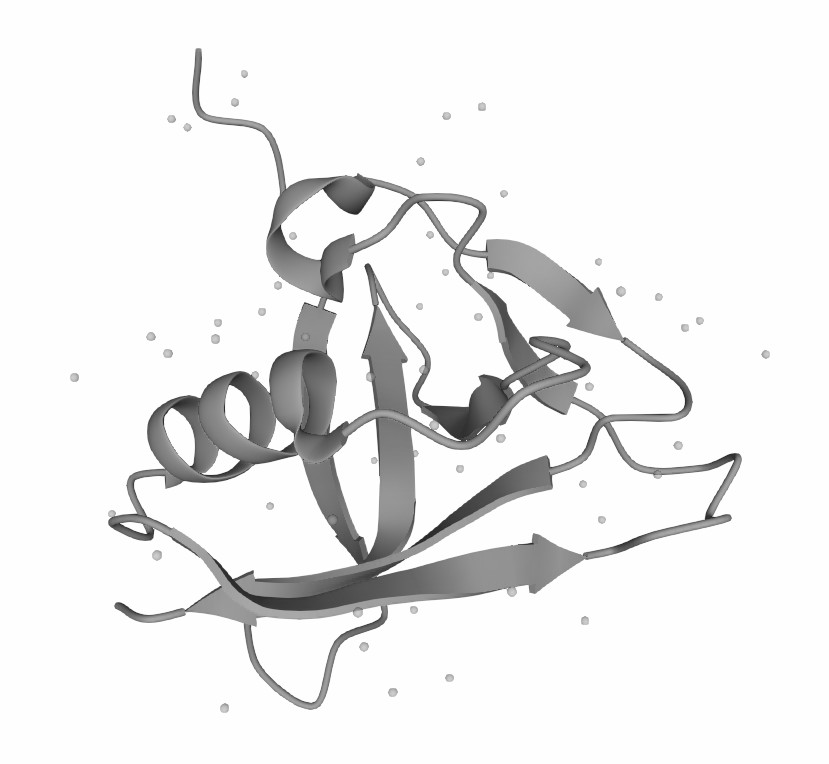 Figure 1. The Structure of Human CD5 (UniProt)1,2.
Figure 1. The Structure of Human CD5 (UniProt)1,2.
The Mechanism of Action of Telimomab
Telimomab is a monoclonal antibody that is specifically designed to interact with CD5 on T-cells. When Telimomab binds to CD5, it initiates a cascade of intracellular signaling reactions that either activate or inhibit T-cell responses. The antibody's binding to CD5 can lead to various biologically significant effects, such as:
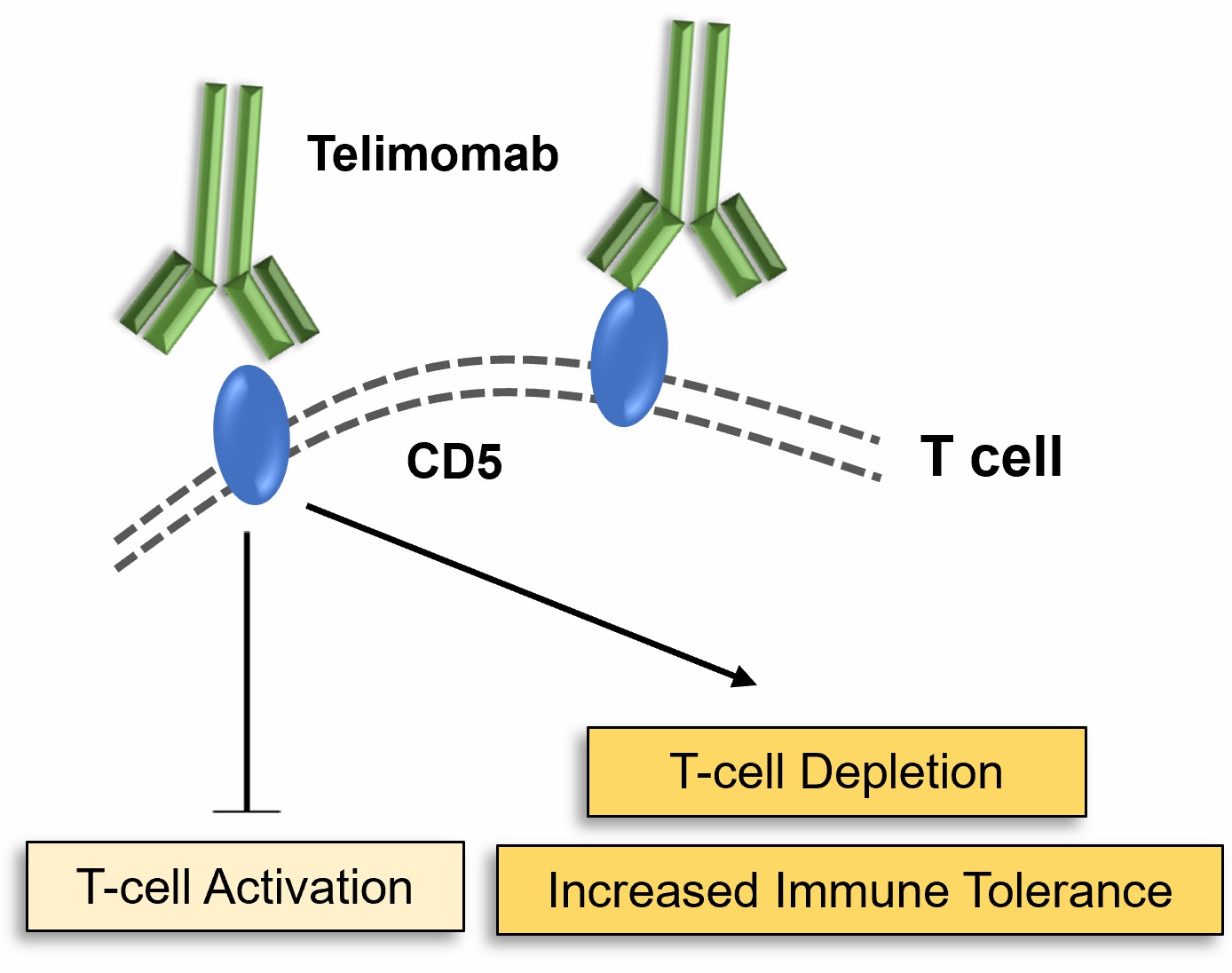 Figure 2. The Mechanism of Action of Telimomab.
Figure 2. The Mechanism of Action of Telimomab.
- Inhibition of T-Cell Activation
Telimomab can deactivate T-cells by interfering with CD5's interaction with the T-cell receptor (TCR). In normal circumstances, TCR interaction with APCs triggers T-cell activation. But CD5 on the surface of T-cells suppresses this activity, "braking" the immune system. By binding to CD5, Telimomab could further increase this inhibitory signal and avoid T-cell overactivation associated with autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. In rheumatoid arthritis, for instance, too many T-cells activate to produce chronic joint inflammation. This modulation is a therapeutic possibility for slowing down inflammation and stemming further damage to the joints, thanks to telimomab.
- Induction of T-Cell Depletion
In some clinical applications, Telimomab can drive T-cell depletion via antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). When the antibody recognizes CD5 on T-cells, it is able to recruit NK (natural killer) cells or macrophages to attack the T-cells. It's especially useful in illnesses where T-cells are involved in pathogenic inflammation or autoimmunity. By destroying particular T-cell populations, Telimomab suppresses the immune response to a large extent and restores immune tolerance. Such a potential application would be in the treatment of T-cell-based autoimmune disorders like multiple sclerosis, in which the immune system attacks the myelin sheath of nerve cells instead. Telimomab may have the ability to suppress autoreactive T-cells, creating a new therapeutic strategy for treating the disease.
- Modulation of Immune Tolerance
One of Telimomab's primary therapeutic objectives is immune tolerance. For most autoimmune disorders, the immune system can't tell itself from non-self, attacking healthy tissue. Telimomab's selective modulation of CD5 activity contributes to the restoration of this tolerance by altering the thresholds of T-cell activation. This activity can keep T-cells from attacking self-tissue, and therefore Telimomab is a candidate for autoimmune diseases. For instance, in autoimmune diseases such as Type 1 diabetes, where T-cells attack pancreatic beta cells, Telimomab could control the T-cells and save them from immune attack.
The Clinical Applications of Telimomab
The specific mechanism of action of Telimomab (which targets CD5) provides a broad therapeutic avenue for a broad range of immune-related diseases. Its current focus has been on autoimmune disorders, but it might also find a niche in cancer immunotherapy and transplantation. Here are a few key areas where Telimomab could play a pivotal role:
Autoimmune Diseases
Telimomab, as mentioned, is especially promising for the treatment of autoimmune disorders. It activates T-cells by attacking CD5 and maintains immune homeostasis, thereby minimizing damaging immune responses. Symptoms in diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and psoriasis involving T-cell dysregulation could be treated with Telimomab.
Cancer Immunotherapy
Another area in which Telimomab may have a good future is in cancer immunotherapy. T-cells are an important part of the immune response against tumors, but cancer cells typically escape immune surveillance by inhibiting T-cell function. With its modulation of CD5, Telimomab may boost T-cell anti-tumor function to possibly decrease tumor growth and improve patient survival. This strategy may be especially useful in cancers in which T-cell exhaustion or immune escape is a major inhibitor of treatment success.
Organ Transplantation
In organ transplantation, Telimomab could help avoid graft rejection. The problem with transplantation is that the immune system can perceive the transplanted organ as foreign and initiate an immune attack against it. By regulating T-cell activity and immune tolerance, Telimomab might mitigate rejection risk and improve graft survival.
What We Provide
Mouse Anti-CD5 Recombinant Antibody (Clone Telimomab); Fab Fragment
We provide high-quality telimomab for use in FuncS, IF, Neut, ELISA, FC, IP, and ICC. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Derivation
- Mouse
- Type
- Mouse Fab
- Specificity
- Human CD5
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Clone
- Telimomab
- Applications
- FuncS, IF, Neut, ELISA, FC, IP, ICC
- UniProt Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P06127/entry)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0] without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



