Dusigitumab Overview
Introduction of Dusigitumab
Dusigitumab, also known as MEDI-573, is a recombinant monoclonal antibody specifically engineered to target and neutralize Insulin-like Growth Factor 2 (IGF2). IGF2 is a peptide hormone playing a pivotal role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival. Its abnormal expression is implicated in numerous malignancies, particularly those involving aberrant growth signaling pathways. Dusigitumab operates by binding IGF2, thereby inhibiting its interaction with its receptors, predominantly IGF-1R and Insulin Receptor A (IR-A), and thus mitigating its pathological effects. Despite its promise, dusigitumab is still under extensive clinical investigation. Ongoing research focuses on optimizing dosing regimens, minimizing potential side effects, and understanding its long-term benefits. Advanced clinical trials aim to solidify its efficacy across different types and stages of cancer and in combination with other therapies. Furthermore, the development of resistance to dusigitumab necessitates a deeper understanding of underlying mechanisms, potentially leading to the design of second-generation antibodies or adjunctive treatments to maintain its clinical effectiveness.
Biological and Chemical Properties of IGF2
Protein Structure
 Figure 1. The Structure of Human IGF2 (UniProt)1,2
Figure 1. The Structure of Human IGF2 (UniProt)1,2
The Mechanism of Action of Dusigitumab
The mechanism of action of dusigitumab is intricate, involving multiple biological processes. The mechanism is explained in detail as follows:
- IGF2 Binding and Neutralization: The primary function of dusigitumab is to bind IGF2 with high affinity and specificity. IGF2 circulates in the extracellular matrix and blood, where it can engage its receptors, IGF-1R and IR-A. By binding to IGF2, dusigitumab prevents these interactions, effectively neutralizing IGF2 and rendering it inactive.
- Inhibition of Downstream Signaling Pathways: IGF2-activated receptors stimulate several downstream signaling cascades, including the PI3K/AKT and MAPK pathways. These pathways underlie multiple cellular activities such as growth, metabolism, and survival. By blocking IGF2, dusigitumab disrupts these pathways, leading to inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis in cancer cells.
- Anti-Angiogenic Effects: IGF2 is known to promote angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels, which is vital for tumor growth and metastasis. Dusigitumab's inhibition of IGF2 also curtails angiogenic signals, resulting in reduced vascularization of tumors, thereby diminishing their growth and metastatic potential.
- Immune Modulation: Beyond direct tumor inhibition, blocking IGF2 may enhance anti-tumor immune responses. The desensitization of IGF2-mediated growth signals can potentiate the immune system's capability to recognize and destroy malignant cells, complementing other immunotherapeutic strategies.
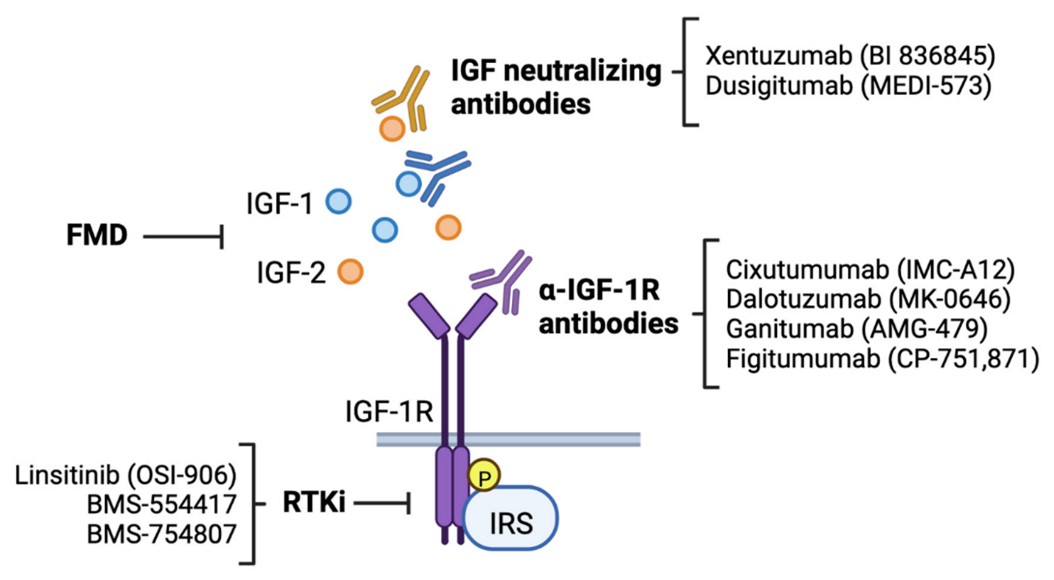 Figure 2. The Mechanism of Action of Dusigitumab3,4
Figure 2. The Mechanism of Action of Dusigitumab3,4
The Clinical Applications of Dusigitumab
Dusigitumab's clinical utility is significant, spanning several cancer types and potentially other IGF2-associated conditions.
- Cancer Therapy: The most prominent application of dusigitumab is in oncology. IGF2 is overexpressed in several cancers, including liver, colorectal, breast, and sarcoma. In liver cancer, for example, elevated IGF2 levels correlate with poor prognosis due to enhanced tumor growth and resistance to conventional therapies. Preliminary clinical trials suggest that dusigitumab can reduce tumor size and improve patient outcomes in these cancers by targeting the IGF2 axis.
- Combination Therapies: Dusigitumab is also explored in combination with other therapeutic modalities. For instance, its use alongside traditional chemotherapies or radiation can potentiate efficacy by simultaneously curbing tumor growth signals and enhancing cytotoxic effects. Moreover, combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors, dusigitumab may help surmount resistance mechanisms, fostering more robust anti-tumor immunity.
- Non-Oncological Diseases: Beyond oncology, dusigitumab holds promise for treating disorders where IGF2 plays a pathological role. For example, high IGF2 levels are implicated in certain metabolic syndromes and growth disorders. Thus, dusigitumab could be repurposed for such conditions, representing a novel therapeutic avenue.
Clinical Projects of Dusigitumab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT01498952 | MEDI-573 in Combination With SOC in Unresectable or Metastatic HCC. | Completed | Unresectable or Metastatic Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) | MedImmune LLC | 2012-01-17 |
| NCT01446159 | Study of MEDI-573 Plus Standard Endocrine Therapy for Women With Hormone-sensitive Metastatic Breast Cancer | Completed | Hormone-sensitive, HER-2 Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer | MedImmune LLC | 2011-06-13 |
| NCT01340040 | Dose-escalation Study to Assess Safety, Tolerability and Pharmacokinetics of MEDI-573 in Japanese Subjects | Completed |
Advanced Solid Malignancies Cancer |
AstraZeneca | 2011-07 |
| NCT00816361 | A Dose-escalation Study to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Antitumor Activity of MEDI-573 in Subjects With Advanced Solid Tumors | Completed | Cancer | MedImmune LLC | 2009-03-09 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=%20MEDI-573
What We Provide
Anti-IGF2 Recombinant Antibody (Dusigitumab)
We provide high-quality dusigitumab for use in Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC, IHC, and most other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Human
- Derivation
- Human
- Type
- IgG2
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC, IHC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 1204390-13-5
- Generic Name
- dusigitumab
- MW
- 151 kDa
- Related Disease
- Breast cancers
- https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P01344/entry#function
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0]. It was not modified and the titles was " The Structure of Human IGF2 (UniProt)".
- Lee, Ji-Sun et al. "The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target." Life (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 12,12 1992. 29 Nov. 2022.
- Images retrieved from Figure 3 " The Insulin-like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: An Elusive Therapeutic Target." Lee, Ji-Sun, 2022, used under [CC BY 4.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). The image was not modified and the title was changed to "The Mechanism of Action of Dusigitumab".
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



