Flanvotumab Overview
Introduction of Flanvotumab
Flanvotumab, with the clinical development code IMC-20D7S, marks a turning point in immuno-oncology. This monoclonal antibody (mAb) binds to Tyrosinase-Related Protein 1 (TYRP1), which triggers cytotoxic T-cell and antibody-mediated immune responses against gp75-expressing melanoma cells, making it a potential treatment for TYRP1-positive melanomas. Preclinical data highlight its potent antitumor effects, particularly its capacity to activate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), which are critical for killing TYRP1-positive melanoma cells. Such results set the stage for clinical testing. Phase I trials evaluated the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of flanvotumab in patients with advanced melanoma. The trials showed that flanvotumab was well tolerated with no severe dose-limiting toxicities. While clinical efficacy (the most common side effect was stable disease), the drug had a good safety profile and an activity mechanism that would make it a good candidate for combination therapies. These findings support the continued development and testing of flanvotumab in larger trials and regimens, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, to further extend its efficacy as a therapeutic agent.
Biological and Chemical Properties of TYRP1
Protein Structure
 Figure 1. The Structure of Human TYRP1 (UniProt)1,2.
Figure 1. The Structure of Human TYRP1 (UniProt)1,2.
The Mechanism of Flanvotumab Action
Understanding TYRP1 and Its Role in Melanoma
Melanoma, a notoriously deadly skin cancer, is highly resistant to standard treatments. Tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TYRP1) is a glycoprotein that plays a critical role in the synthesis of melanin and is mostly found in melanocytes. Beyond its pigmentogenic function, TYRP1 is abundantly expressed in melanoma cells and is a stable biomarker throughout melanoma development. TYRP1 also contributes to immune evasion, making melanoma cells more resistant to oxidative stress and more resilient. Because TYRP1 is located on the surface of melanoma cells and is not expressed in non-malignant tissue, it represents an excellent target for monoclonal antibody (mAb) therapies. By specifically targeting TYRP1, flanvotumab not only disrupts melanoma cell activity but also activates immune mechanisms (for example, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)) to inhibit tumour growth.
How Does Flanvotumab Work?
Flanvotumab is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to TYRP1 in melanoma cells. Its mechanisms of action include:
- Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Flanvotumab recruits natural killer (NK) cells to the tumor site by binding to their Fc receptors. Once attached, NK cells release cytotoxic granules that kill TYRP1-expressing melanoma cells. Flanvotumab, for instance, exhibited ADCC activity in preclinical studies, effectively lowering tumor burden in murine melanoma models.
- Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC)
Flanvotumab activates the complement cascade upon binding to TYRP1, which forms membrane attack complexes that kill melanoma cells. This dual action boosts its effectiveness and emphasizes its potential as an outpatient or combination treatment.
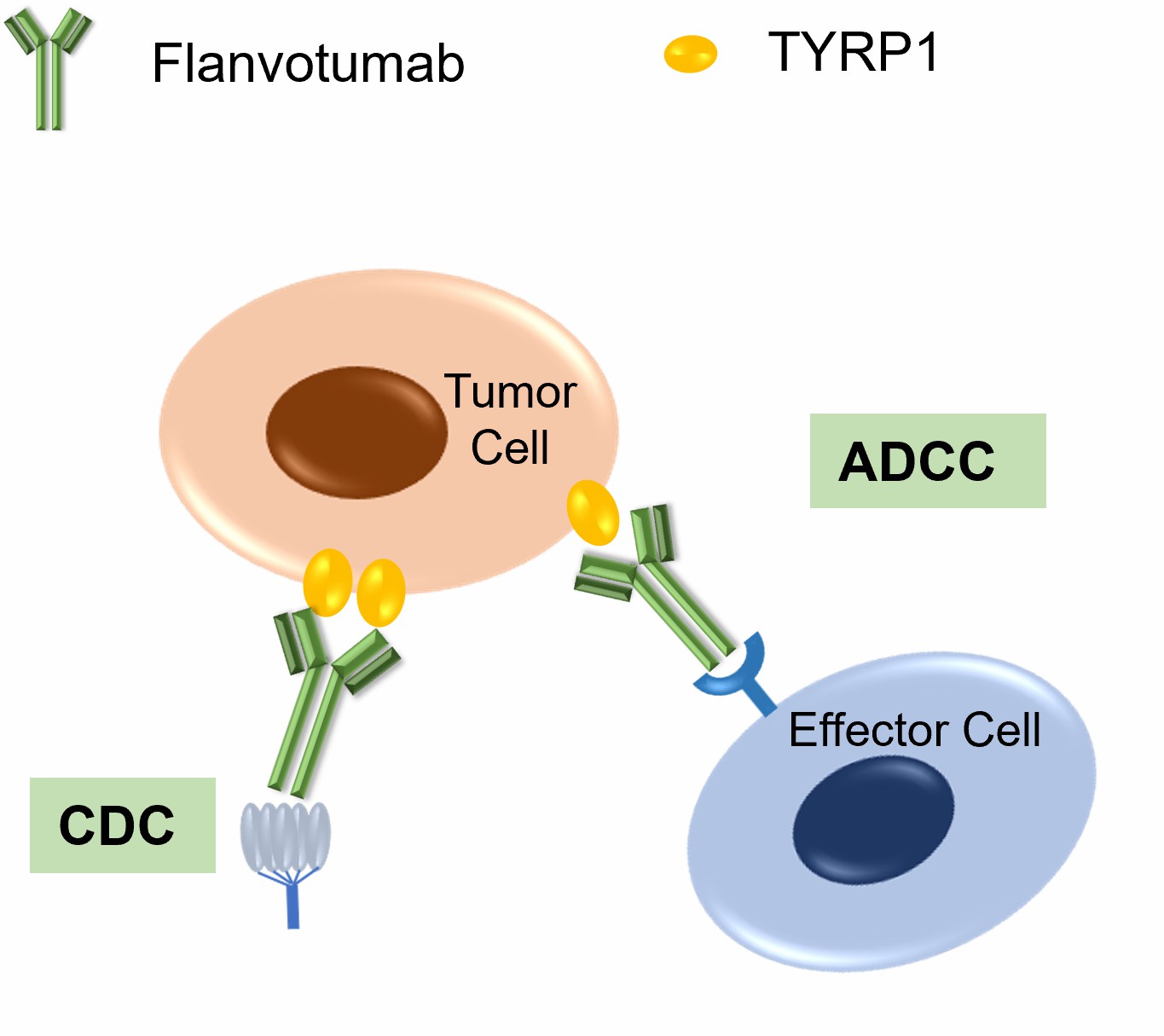 Figure 2. The Mechanism of Flanvotumab Action.
Figure 2. The Mechanism of Flanvotumab Action.
The Clinical Applications of Flanvotumab
Precision Targeting in TYRP1-Positive Melanoma
Flanvotumab's ability to specifically target TYRP1 offers a tailored approach to treating TYRP1-positive melanoma. This precision minimizes off-target effects and ensures the effective activation of ADCC and CDC, which are critical for eradicating melanoma cells.
Combination Therapy Potential
Flanvotumab shows promise when used in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-CTLA-4 antibodies. This strategy enhances immune responses by addressing multiple pathways of immune evasion in resistant or advanced melanoma.
Maintenance Therapy
By targeting the stable TYRP1 expression, flanvotumab may serve as a maintenance therapy to extend remission and delay progression in patients who achieve disease stability following initial treatment.
Addressing Rare Subtypes
Flanvotumab's applicability extends to challenging melanoma subtypes, such as mucosal and uveal melanomas, where TYRP1 expression is prevalent but treatment options are limited.
Personalized Medicine
Flanvotumab aligns with personalized oncology by enabling treatment selection based on TYRP1 expression, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing unnecessary interventions.
Clinical Projects of Flanvotumab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT01137006 | An Open-Label, Dose-Escalation Study of IMC-20D7S In Participants With Malignant Melanoma | Completed | Malignant Melanoma | Eli Lilly and Company | 2010-06-04 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT01137006?cond=IMC-20D7S&rank=1
What We Provide
Anti-Human TYRP1 Recombinant Antibody (Flanvotumab)
We provide high-quality flanvotumab for use in ELISA, FC, IP, FuncS, IF, Neut, ICC, and most other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Human
- Derivation
- Human
- Type
- IgG1 - kappa
- Specificity
- Tested positive against native human antigen.
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in ELISA, FC, IP, FuncS, IF, Neut, ICC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 1188277-05-5
- Generic Name
- Flanvotumab
- UNII
- M76FX2JZRM
- MW
- 145.5 kDa
- Related Disease
- Malignant melanoma
- UniProt Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P17643/entry)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0] without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

