Oxelumab Overview
Introduction of Oxelumab
Oxelumab, a pioneering human monoclonal antibody engineered by Genentech, a Roche subsidiary, stands at the forefront of immunotherapy. This innovative treatment specifically targets the OX40L-OX40 interaction, a crucial pathway in the immune system. By disrupting the binding of OX40L (CD252) to its receptor OX40 (CD134) on T cells, oxelumab effectively dampens the immune response, making it a potential game-changer in managing inflammatory diseases like asthma. Initiated in September 2009, the first clinical trials of oxelumab meticulously evaluated its efficacy, safety, and tolerability in preventing allergen-induced airway obstruction among adults with mild allergic asthma, marking a significant milestone in allergy and asthma research.
The Mechanism of Action of Oxelumab
CD252, also known as OX40L or TNFSF4 (Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily member 4), is a protein that plays a crucial role in the immune system. It is primarily expressed on the surface of antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, B cells, and activated endothelial cells. CD252 interacts with its receptor OX40 (CD134) on T-cells, promoting T-cell proliferation, survival, and cytokine production. This interaction is essential for effective immune responses, particularly in enhancing the function of CD4+ T cells and regulating immune tolerance and memory formation. Oxelumab blocks the interaction between CD252 and its receptor OX40 on T cells. This inhibition prevents the activation and proliferation of T cells, which is crucial in reducing inflammatory responses. The suppression of this pathway can be particularly beneficial in treating autoimmune diseases and conditions where the immune system is inappropriately activated, thereby reducing tissue damage and inflammation.
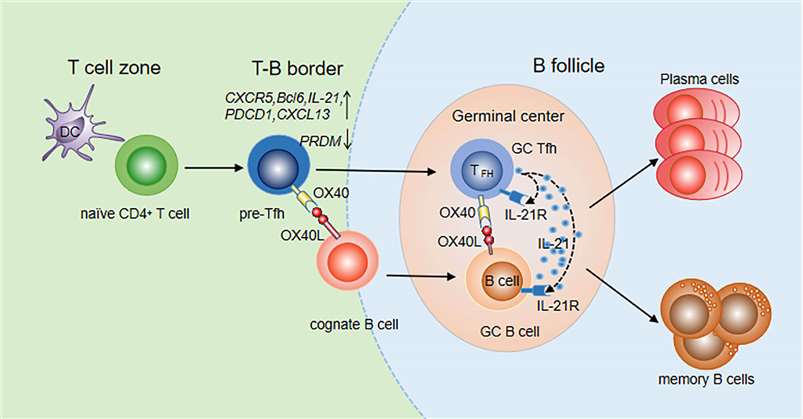 Figure 1. The Mechanism of Action of Oxelumab(Fu, 2021)
Figure 1. The Mechanism of Action of Oxelumab(Fu, 2021)
OX40L (OX40 ligand) and OX40 (CD134) are critical components of the immune system, belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily. The interaction between OX40L and OX40 is pivotal in regulating immune responses, particularly in T cell activation, proliferation, and survival.
The binding of OX40L to OX40 triggers several key signaling pathways that regulate T cell function.
NF-κB Pathway:
The interaction between OX40 and OX40L recruits TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs), particularly TRAF2 and TRAF5. This leads to the activation of the IκB kinase (IKK) complex, resulting in the phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, which releases NF-κB. Activated NF-κB translocates to the nucleus, promoting the expression of various cytokines and anti-apoptotic genes such as Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL, enhancing T cell survival and function.
PI3K/Akt Pathway:
OX40 activation can also stimulate phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) via TRAF proteins. PI3K converts PIP2 to PIP3, which subsequently activates protein kinase B (Akt). Akt promotes cell survival, proliferation, and metabolic activity by inhibiting pro-apoptotic proteins such as Bad and Caspase 9, thus protecting T cells from apoptosis.
MAPK Pathway:
The OX40-OX40L interaction can activate members of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) family, including ERK1/2, JNK, and p38 MAPK. These kinases regulate gene expression, cell division, and differentiation, further enhancing T cell functionality and survival.
The OX40L-OX40 interaction serves several crucial roles in immune responses:
Enhanced T Cell Activity and Survival:
Through the aforementioned signaling pathways, OX40L-OX40 interaction boosts the activation, proliferation, and survival of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.This process is essential for effective immune responses, memory T cell formation, and long-term immune surveillance.
Regulation of Immune Tolerance:
OX40L-OX40 interaction plays a vital role in maintaining immune system balance, and preventing excessive or erroneous immune reactions. In autoimmune and inflammatory diseases, overactivation of OX40 can lead to the immune system attacking self-tissues.
Involvement in Cancer Immune Surveillance:
The OX40 signaling pathway is critical in enhancing anti-tumor immune responses, particularly in T cell-mediated tumor clearance.
By activating T cells, OX40 can promote anti-tumor activity, making it a potential target for cancer immunotherapy.
Biological and Chemical Properties of Teplizumab
Protein Chemical Formula
C6424H9920N1704O2014S42
Protein Average Weight
144.6 kDa (peptide)
- Fu, NanNan, et al. "The OX40/OX40L Axis Regulates T Follicular Helper Cell Differentiation: Implications for Autoimmune Diseases." Frontiers in immunology vol. 12 670637. 21 Jun. 2021. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

