Polatuzumab Overview
Introduction of Polatuzumab
Polatuzumab is a genetically engineered antibody specifically designed to target CD79b, a protein embedded in the membrane of B-cells. As a key component of the B-cell receptor (BCR) complex, CD79b is essential for initiating and propagating B-cell receptor signaling. It is ubiquitously expressed in B-cell malignancies, such as Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), making it a promising therapeutic target. Polatuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to CD79b, disrupting BCR signaling and thereby inhibiting the growth and survival of tumor cells. This antibody can also be conjugated with monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE), a microtubule-disrupting toxin, to form an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), which effectively and selectively kills CD79b-expressing tumor cells in some in vitro models. Furthermore, ongoing clinical trials aim to assess the long-term benefits, safety profiles, and potential integration into existing therapeutic regimens. The specificity and potency of this antibody hold promise for CD79b-positive malignancies, paving the way for broader applications in oncology.
Biological and Chemical Properties of CD79b
Protein Structure
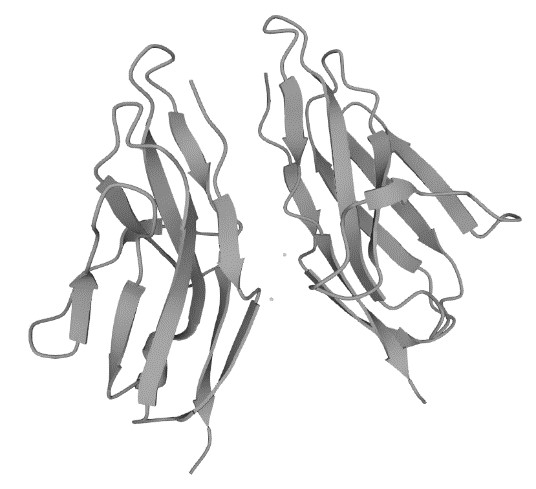 Figure 1. The Structure of Human CD79b (UniProt)1,2
Figure 1. The Structure of Human CD79b (UniProt)1,2
The Mechanism of Polatuzumab Action
CD79b, also known as Igβ, belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily, along with CD79a (Igα). As crucial components of the BCR complex, these two proteins are non-covalently associated through disulfide bonds to form the signaling heterodimer of the BCR, playing a pivotal role in BCR signaling and the subsequent immune response. Structurally, the extracellular domain of CD79b interacts with Igα, while its intracellular domain features an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) that can be phosphorylated by Src-family kinases, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways such as PI3K/AKT and NF-κB and participating in BCR signal transduction. CD79b is implicated in a variety of B-cell-related diseases, including Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (NHL), Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL), and Waldenström Macroglobulinemia (WM) in which its expression levels and functionality may be altered inordinately. Specifically, mutations in CD79b in malignant B-cells in may lead to constitutive activation of signaling pathways, thereby promoting tumor cell growth and survival. For instance, mutations in CD79b are correlated with the development and progression of certain types of DLBCL, potentially enhancing BCR signaling and promoting the survival and proliferation of tumor cells. In CLL, the expression levels of CD79b may influence disease progression and response to therapy.
As part of the BCR signaling pathway, CD79b is a potential therapeutic target for B-cell-related diseases. By specifically binding to CD79b, polatuzumab optimally localizes to pathologically proliferative B-cells, and this specificity spares non-target cells, protecting them from attack. In addition to its target-drug binding, polatuzumab available on our website stands out for its modification of the Fc region to enhance ADCC (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity). This modification increases its affinity for Fcγ receptors on effector cells like natural killer (NK) cells, macrophages, and neutrophils. Once the Fab region of the antibody binds to CD79b on the target B-cell, the enhanced Fc region interacts robustly with Fcγ receptors on effector cells, triggering downstream cytotoxicity induction and amplifying immunogenic cell death.
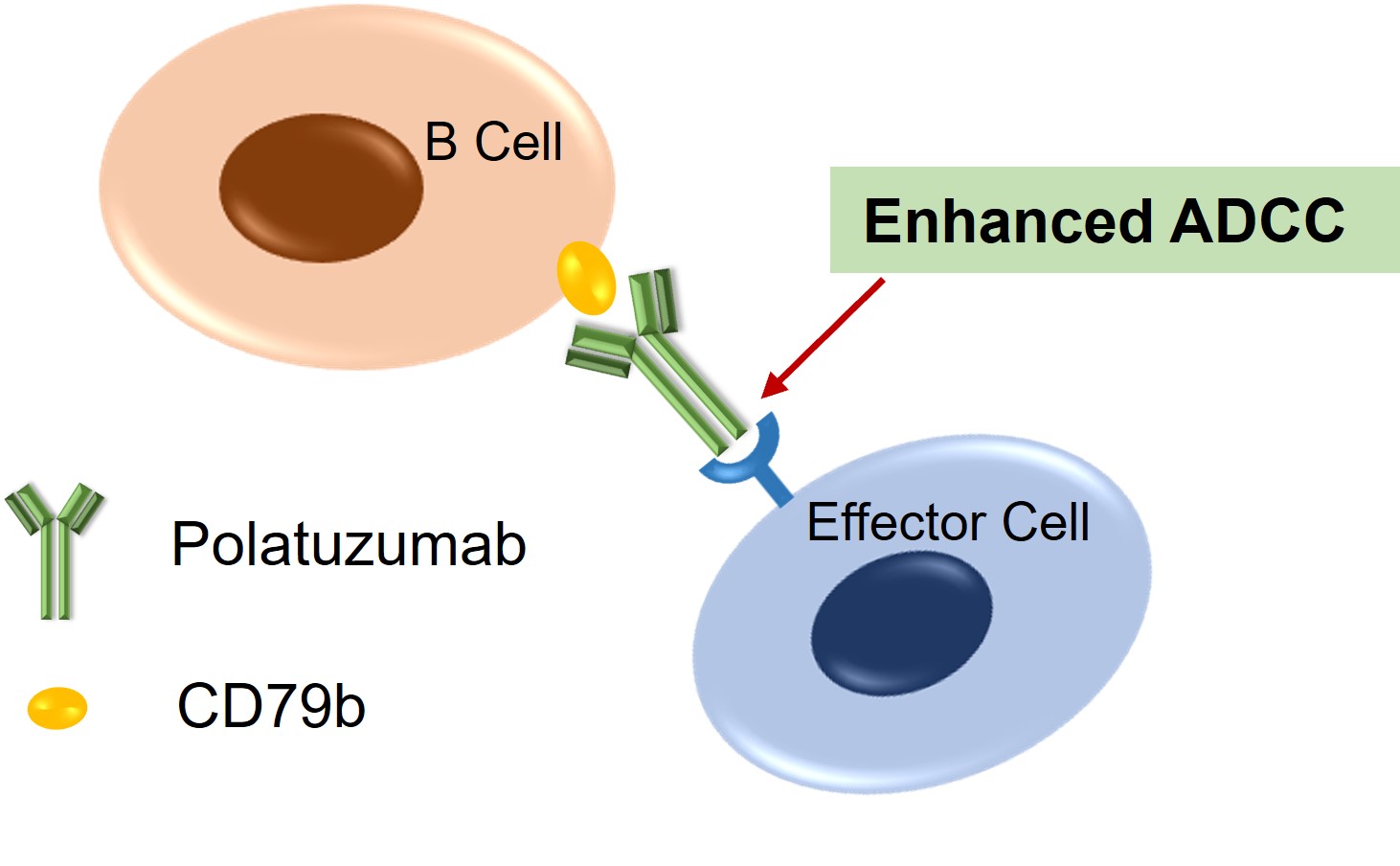 Figure 2. The Mechanism of Polatuzumab Action (Creative Biolabs Original)
Figure 2. The Mechanism of Polatuzumab Action (Creative Biolabs Original)
Clinical Projects of Polatuzumab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT05615636 | A Phase II Trial of Mosunetuzumab, Polatuzumab, Tafasitamab, and Lenalidomide in Patients With Relapsed B-cell NHL | RECRUITING |
B-Cell Lymphoma Hodgkin Lymphoma Relapsed B-cell NHL |
M.D. Anderson Cancer Center | 2023-04-28 |
| NCT05868395 | Efficacy of Polatuzumab, Bendamustine and Rituximab in Patients With Relapsed/ Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma | RECRUITING | Mantle-cell Lymphoma | Medical University of Vienna | 2024-01-02 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=Polatuzumab
- Uniprot Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P40259/entry#structure)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0]. It was not modified and the titles was " The Structure of Human CD79b (UniProt)".
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

