TCR Signaling Pathway
About TCR pathway
T-cell receptor (TCR) is a heterodimers composed of α and β peptide chains. TCR is mainly responsible for recognizing the antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APC). TCR forms immune synapse between T cells and APC by cell-cell interaction mediated by associated costimulatory molecules and integrin, resulting in cascade reaction of downstream signals and regulating the cells through the cytokines. The cytoplasmic region of TCR is short and needs to covalently bind with CD3 (composed of CD3 ε, γ and δ chains and TCR ζ chain) to form a TCR/CD3 complex to transmit signals. The immuno-receptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) in the cytoplasmic region of CD3 play an important role in TCR signal transduction. When TCR binds to antigen, costimulatory molecules such as CD45 modulates the phosphorylation and activation of Lck and other Src tyrosine kinases. Activated Lck binds to the cytoplasmic regions of CD4 or CD8 molecules in T cells, and is recruited to the TCR complex with CD4 or CD8, phosphorylating ITAMs on the cytoplasmic side of the TCR complex. Phosphorylated ITAMs recruits and phosphorylates Zeta chain-associated protein kinases (ZAP-70), thereby facilitating recruitment and phosphorylation of downstream adapters or scaffold proteins, including the transmembrane adapter LAT (Linker Activator for T-Cells). LAT is the key scaffold proteins in TCR pathway. Phosphorylated LAT recruits downstream molecules such as Grb2 (growth factor receptor-bound protein 2), GADS (GRB2-related adapter protein 2), phospholipase C-γ1 (PLC-γ1) to form LAT signalosome, a signal transduction complex. The adaptor protein SLP-76 and IL2-inducible T-cell kinase (ITK) can be recruited by GADS. Then, Phosphorylated ITK activates PLC-γ1, decomposing phosphorylating phosphatidylinositol-4, 5-bisphosphate (PIP2) on cell membrane to produce second messenger diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol trisphosphate (IP3). IP3 binds IP3 receptor to activate endoplasmic reticulum calcium channels and release endoplasmic reticulum calcium ions into the cell. The decrease of endoplasmic reticulum calcium concentration further promotes the opening of calcium channels on the cell membrane, resulting in extracellular calcium influx. The increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentration can activate calcineurin, catalyze the dephosphorylation and entry of transcription factor NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T cell) into the nucleus, mediating the expression of downstream genes. Additionally, DAG can activate the MAPK Signaling Pathway and activate the transcription factor AP1 (activator protein 1) and NF-κB through PKC to regulate the expression of target genes.
Related Pathways
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


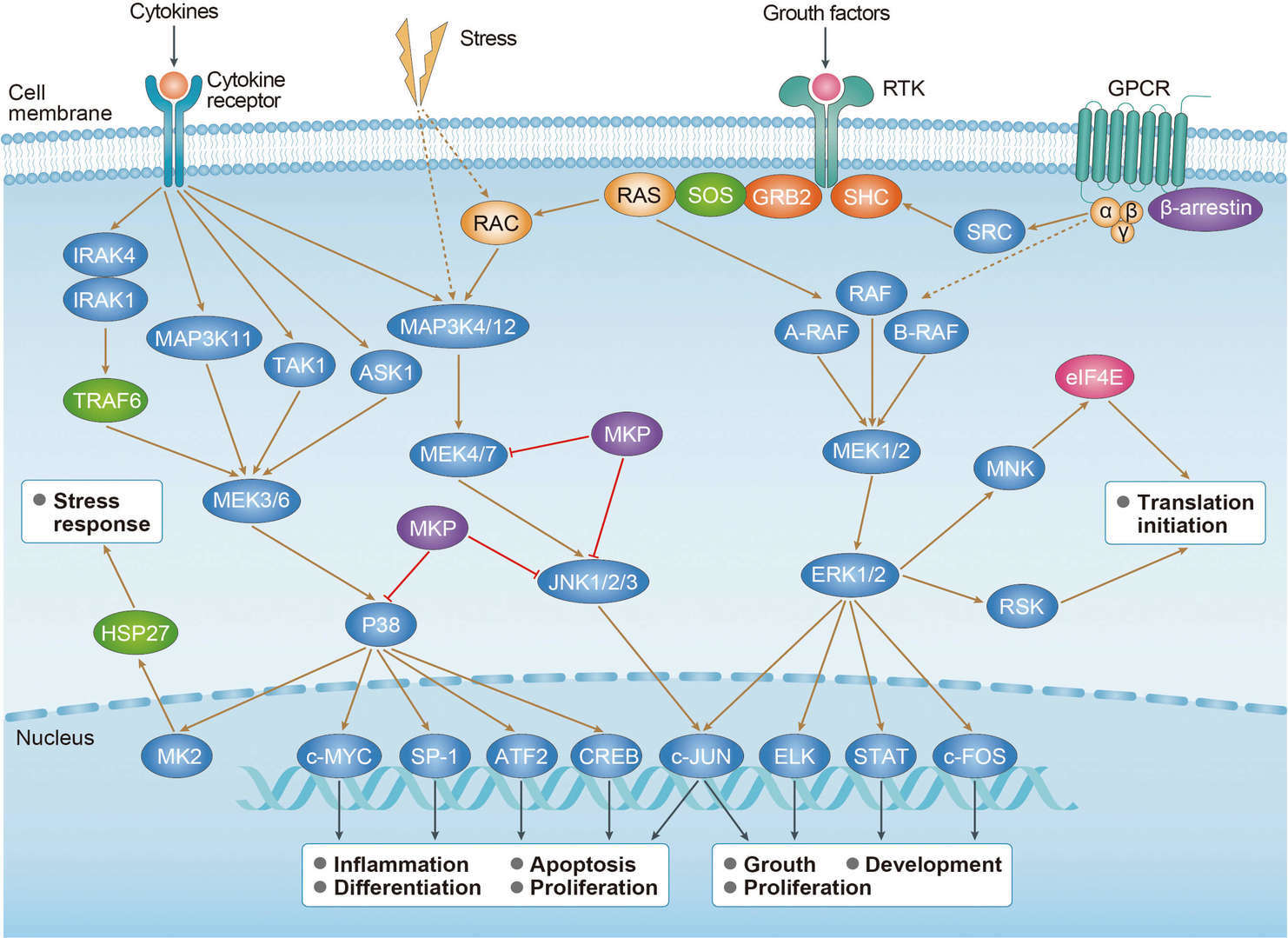 MAPK Signaling Pathway
MAPK Signaling Pathway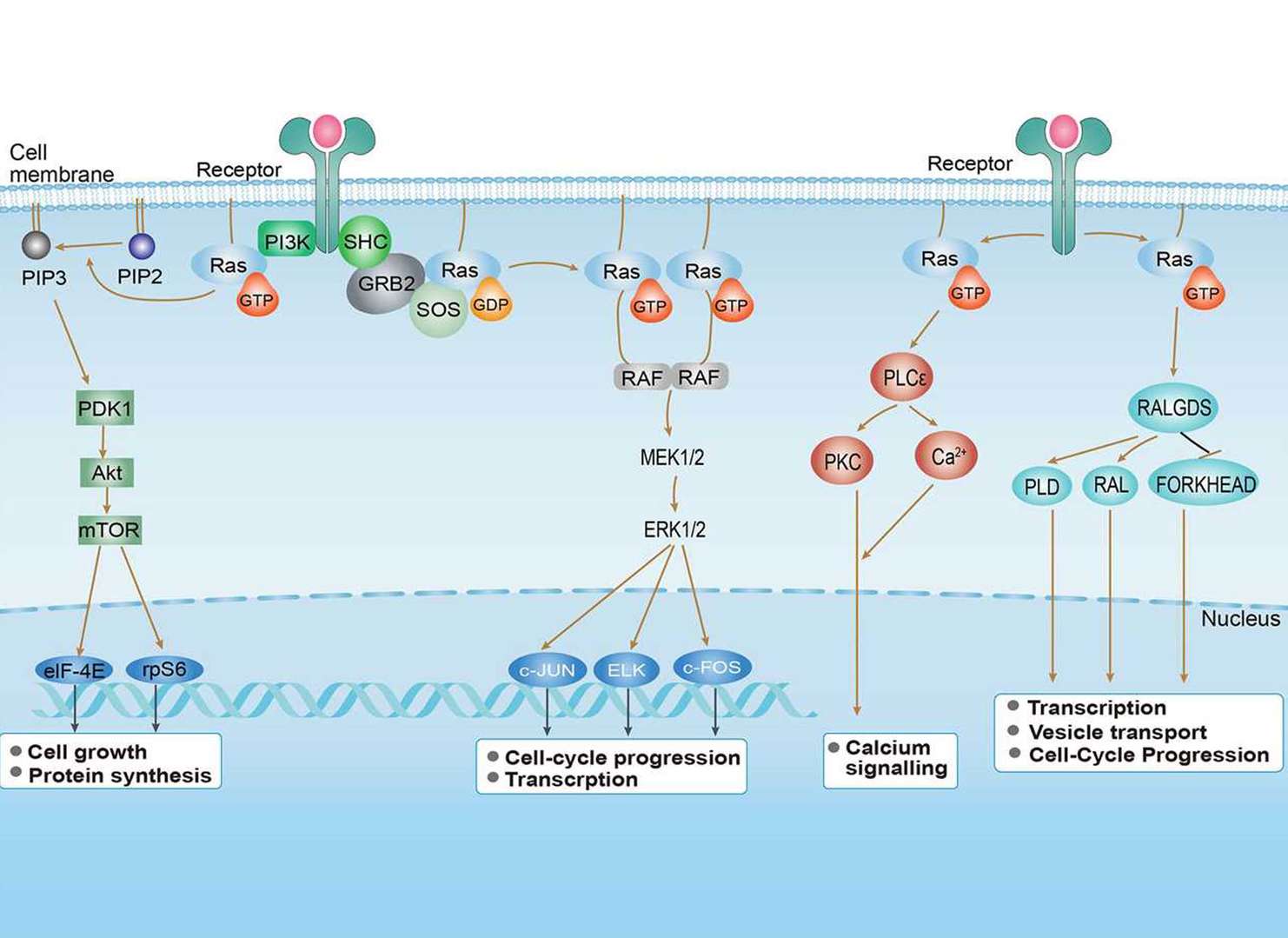 Ras Signaling Pathway
Ras Signaling Pathway