Detumomab Overview
Introduction of Detumomab
Detumomab is a recombinant monoclonal antibody that targets unreported B-cell lymphoma tumor-associated antigens (TAA) found on the surface of B-cell lymphoma cells. This binding inhibits TAA-mediated signaling and leads to tumor cells death. Detumomab's molecular structure is similar to other IgG-class antibodies, composed of two heavy chains and two light chains with constant and variable sections respectively. Detumomab's specificity is due to its variable sections that engage with distinct epitopes on B cell lymphoma cells which is considered a vital type of white blood cell in immune system. Diverse hematologic cancers known as B cell lymphomas are induced by B lymphocytes. Therefore, the use of anti-B cell lymphoma recombinant monoclonal antibodies targeting B lymphocytes primarily associated with B cell lymphomas has revolutionized therapeutic techniques, resulting in significant therapeutic outcomes.
The Mechanism of Action of Detumomab
The mechanism of action of detumomab is multifaceted and involves several key immunological processes:
-
Target Recognition and Binding:
Detumomab's mode of action is complicated, involving multiple critical immunological pathways. One critical component is the identification and binding of specific epitopes on the surface of B cell lymphoma cells. Detumomab is intended to target epitopes that are unique or overexpressed in B cell malignancies, such as CD20, CD19, and other B cell-specific markers. -
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC):
After attaching to its target antigen, detumomab's Fc region interacts with Fc receptors on natural killer (NK) cells, resulting in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). This connection causes NK cells to secrete cytotoxic granules containing perforin and granzymes. These chemicals cause apoptosis in the targeted B cell lymphoma cells by damaging their membranes. -
Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC):
Detumomab can also activate the complement cascade via its Fc region, causing complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC). The binding of the complement component C1q to the Fc region sets off a cascade of proteolytic events that culminate in the creation of the membrane attack complex (MAC). The MAC breaks the cell membrane of lymphoma cells, causing lysis and death. -
Direct Induction of Apoptosis:
In certain cases, detumomab can also directly cause apoptosis in addition to these indirect methods. It uses inherent mechanisms to transfer pro-apoptotic signals into lymphoma cells when it attaches itself to its target antigen on those cells. This causes the lymphoma cells to undergo programmed cell death by activating caspases and releasing cytochrome c from their mitochondria. -
Phagocytosis:
Moreover, detumomab-bound lymphoma cells can be identified by macrophages via Fc receptors. This connection stimulates macrophages to engulf and phagocytose antibody-tagged cancerous cells. Detumomab improves immune clearance mechanisms against B cell lymphomas by promoting phagocytosis.
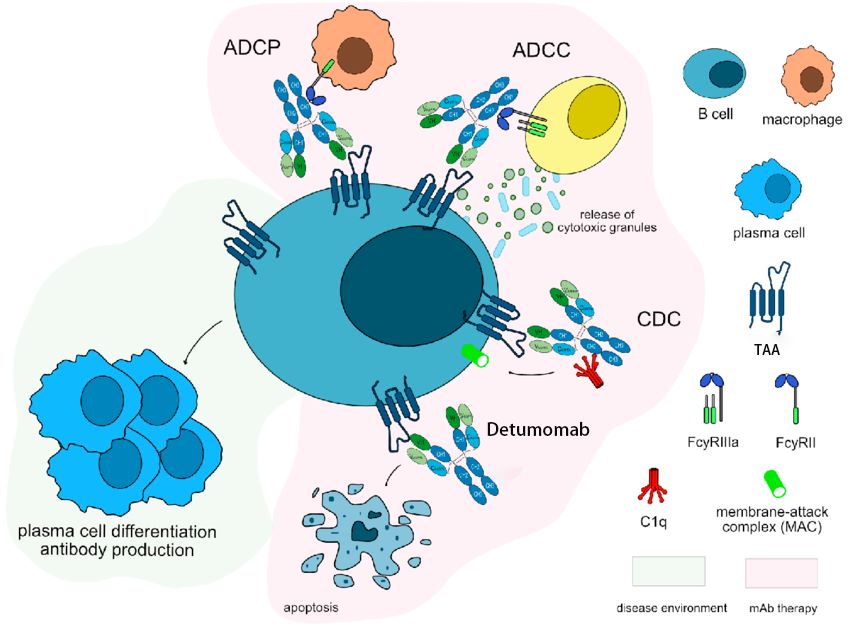 Figure 1. The Mechanism of Action of Detumomab1,2
Figure 1. The Mechanism of Action of Detumomab1,2
Clinical Applications of Detumomab
Detumomab has important implications for the treatment of B cell lymphomas, a kind of hematological malignancy with a wide range of symptoms but a single common cause: B cells. Its clinical applications can be understood by examining its use at various stages of disease progression, combinatorial therapy, and ongoing clinical trials.
- Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory B Cell Lymphomas: Detumomab has shown remarkable efficacy in patients with relapsed or refractory B cell lymphomas. Patients who have not responded to standard medicines such as chemotherapy or radiotherapy may benefit from detumomab's tailored activity. Clinical trials have demonstrated that detumomab can elicit remission in such difficult patients by targeting cancerous B cells.
- Combination Therapies: Detumomab's therapeutic potential is typically increased when used in conjunction with other medications. For example, combining detumomab with chemotherapeutic medicines, immunomodulatory medications, or other monoclonal antibodies has demonstrated synergistic results. As several mechanisms of action are used to target the lymphoma, this combination approach has the potential to enhance overall survival rates while decreasing relapse rates.
- Prophylactic Uses in High-Risk Populations: Detumomab may be used prophylactically in high-risk populations, such as those with a strong family history of B cell lymphomas or those with genetic predispositions. Detumomab, which targets pre-malignant B cells, has the potential to postpone or halt the progression of overt lymphoma.
- Maintenance Therapy: Following remission, detumomab maintenance medication can assist in maintaining the therapeutic response and preventing relapse. Long-term disease control can be achieved with detumomab therapy, which constantly targets and eliminates leftover malignant B cells.
- Emerging Clinical Trials: Numerous clinical trials are now underway to investigate novel applications for detumomab. These trials are looking into different dose regimes, combinations with novel medicines, and detumomab's efficacy in diverse subtypes of B cell lymphomas. Such research initiatives aim to improve the usage of detumomab and broaden its applications, potentially providing new hope for patients with these difficult cancers.
Clinical Projects of Detumomab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT00036426 | Idiotype Vaccine for Low-Grade Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma | UNKNOWN STATUS | Lymphoma, Low-Grade | Favrille | 2001-03 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT00036426?term=NCT00036426&rank=1
What We Provide
Anti-B Cell Lymphomas Recombinant Antibody (Detumomab)
We provide high-quality detumomab for use in IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, IHC, and most other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Derivation
- Mouse
- Type
- IgG1
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, IHC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 145832-33-3
- Generic Name
- detumomab
- Related Disease
- Cancers
- Golfinopoulou, Rebecca et al. "Delving into Molecular Pathways: Analyzing the Mechanisms of Action of Monoclonal Antibodies Integrated in IMGT/mAb-DB for Myasthenia Gravis." Vaccines vol. 11,12 1756. 26 Nov. 2023.
- Images retrieved from Figure 4 "Delving into Molecular Pathways: Analyzing the Mechanisms of Action of Monoclonal Antibodies Integrated in IMGT/mAb-DB for Myasthenia Gravis." Golfinopoulou, Rebecca, 2023, used under [CC BY 4.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). The image was modified and its modifications including: the text "MS4A1" was changed to "TAA" and the text "rituximab" was changed to "Detumomab", and title was changed to "The Mechanism of Action of Detumomab".
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



