-
Supports
- FAQs
- Resources
- Engineered Antibody Overview
- Therapeutic Antibody Overview
- Why Recombinant Monoclonal Antibodies?
- Biosimilars of Monoclonal Antibodies
- Vβ 8 & M2 BsAb Overview
- Ascrinvacumab Overview
- Priliximab Overview
- Arcitumomab Overview
- Altumomab Overview
- Sulesomab Overview
- Besilesomab Overview
- Sevirumab Overview
- Lacnotuzumab Overview
- Urtoxazumab Overview
- Briakinumab Overview
- Certolizumab Pegol Overview
- Efalizumab Overview
- Obiltoxaximab Overview
- Odulimomab Overview
- Ralpancizumab Overview
- Sofituzumab Vedotin Overview
- Tezepelumab Overview
- Refanezumab Overview
- Abciximab Overview
- Rovelizumab Overview
- Vatelizumab Overview
- Edobacomab Overview
- Efungumab Overview
- Nebacumab Overview
- Parsatuzumab Overview
- Bapineuzumab Overview
- Capromab Pendetide Overview
- Dinutuximab Overview
- Duligotuzumab Overview
- Elgemtumab Overview
- Polatuzumab Vedotin Overview
- Ponezumab Overview
- Vorsetuzumab Mafodotin Overview
- Vorsetuzumab Overview
- Olendalizumab Overview
- Afelimomab Overview
- Anatumomab Mafenatox Overview
- Blosozumab Overview
- Brentuximab Vedotin Overview
- Carotuximab Overview
- Denosumab Overview
- Enavatuzumab Overview
- Icrucumab Overview
- Indatuximab Ravtansine Overview
- Infliximab Overview
- Iratumumab Overview
- Lerdelimumab Overview
- Roledumab Overview
- Satumomab Overview
- Satumomab Pendetide Overview
- Siplizumab Overview
- Lifastuzumab Vedotin Overview
- Minretumomab Overview
- Motavizumab Overview
- Naptumomab Estafenatox Overview
- Ozanezumab Overview
- Palivizumab Overview
- Tefibazumab Overview
- Tenatumomab Overview
- Afasevikumab Overview
- Andecaliximab Overview
- Anrukinzumab Overview
- Apolizumab Overview
- Bertilimumab Overview
- Cantuzumab Mertansine Overview
- Clenoliximab Overview
- Codrituzumab Overview
- Dezamizumab Overview
- Ecromeximab Overview
- Eldelumab Overview
- Enoblituzumab Overview
- Enokizumab Overview
- Ensituximab Overview
- Fezakinumab Overview
- Inolimomab Overview
- Keliximab Overview
- Lorvotuzumab Mertansine Overview
- Ontuxizumab Overview
- Otlertuzumab Overview
- Panobacumab Overview
- Pascolizumab Overview
- Pemtumomab Overview
- Plozalizumab Overview
- Prezalumab Overview
- Ramucirumab Overview
- Samalizumab Overview
- Yttrium (90 Y) Clivatuzumab Tetraxetan Overview
- Disease Overview
- Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunoblotting Protocol & Troubleshooting
- 3D Immunohistochemistry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Electron Microscopy Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Spot Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Flow Cytometry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Functional Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Gel Super Shift Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Activation Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Antibody Depletion Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Apoptosis Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Bioimaging Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Blocking Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Cell Screening Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Cell Separation Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Chromatin Immunoprecipitation Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Complement Mediated Cell Depletion Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Costimulation Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Hemagglutination Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunohistology-Resin Section Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunoprecipitation Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunoradiometric Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- In Situ Hybridization Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Intracellular Staining for Flow Cytometry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Cytotoxicity Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Dot Blot Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Mass Cytometry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Knockout/Knockdown Target Confirmation by Western Blot Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Radial Immunodiffusion Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Radioimmunoassay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Surface Plasmon Resonance Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunocytochemistry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunodiffusion Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunofluorescence Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunohistochemistry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunohistochemistry-Frozen Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunohistochemistry-Paraffin Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Immunoassay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Live Cell Imaging Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Multiplex Bead based Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Neutralization Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Protein Purification Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Tissue Culture Protocol & Troubleshooting
- Turbidimetry Protocol & Troubleshooting
- SDS-PAGE
- Western Blot
- Webinars
FcεR1 Signal pathway
About FcεR1 Pathway
The interaction between IgE receptor (FcεRI)-bound IgE and antigen induces an elaborate network of signal transduction pathways that trigger cell activation. The FcεR1 consists of an IgE-binding α chain, a β chain and a disulfide-linked γ chain homodimer. The cytoplasmic tails of β and γ subunits both contain ITAMs, which are the target of Src and Syk family protein tyrosine kinases. FcεRI is involved in the phosphorylation of Lyn and Fyn receptor ITAM, thus generating docking sites for these proteins as well as for Syk. Binding to ITAM results in up-regulation of Fyn, Lyn and Syk kinase activity and phosphorylation of downstream signal molecules. The consequence of these events is the formation of multi-protein complexes containing various signal molecules, which induce the activation of MAPK pathway and the generation of second messenger molecules, thus inducing cell activation. The FcεRI signaling pathway leads to degranulation of mast cells or basophils and release of inflammatory mediators through crosslinking of IgE-antigen complexes.
Related Pathways
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


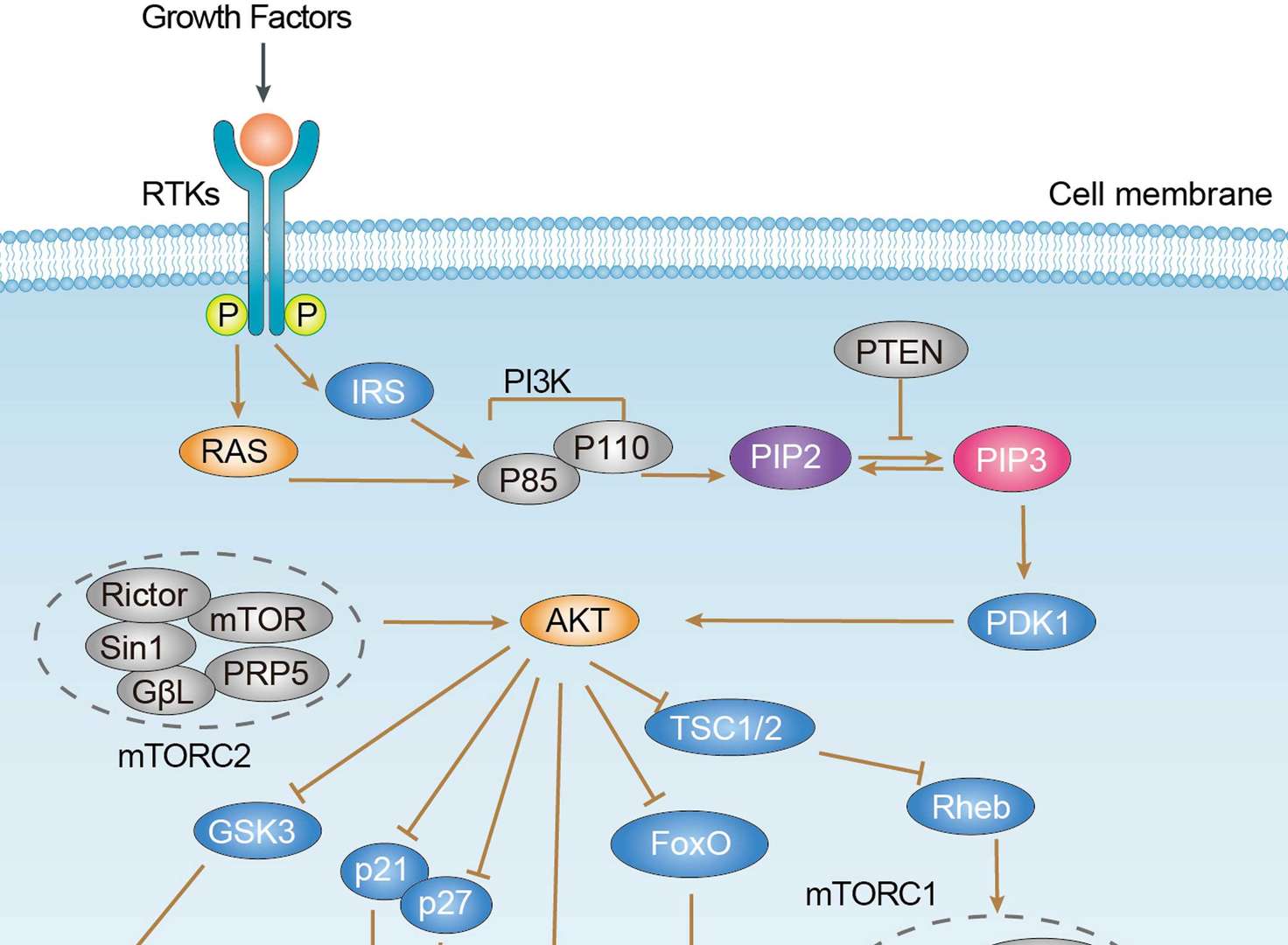 PI3K-Akt Pathway
PI3K-Akt Pathway