Gomiliximab Overview
Introduction of Gomiliximab
Gomiliximab (Lumiliximab or IDEC-152) is a humanized monoclonal antibody designed to specifically block CD23, a low-affinity IgE receptor (FcεRII). This antibody has been shown to control allergic diseases, including asthma and rhinitis, and some B-cell tumors, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). CD23 is pivotal in IgE regulation, making it a critical focus for diseases where IgE and its downstream pathways are implicated. Creative Biolabs has focused on monoclonal antibodies such as Gomiliximab extensively and on CD23-targeting as a therapeutic tool in immune regulation and oncology.
CD23: The Key to Immune Regulation
CD23 might not be as famous as some other immune molecules, but its role is critical. Found on the surface of B cells, monocytes, and other immune cells, it regulates IgE, the antibody responsible for many allergic reactions. It also exists in a soluble form (sCD23), which can amplify inflammatory responses.
 Figure 1. The Structure of Human CD23 (UniProt)1,2.
Figure 1. The Structure of Human CD23 (UniProt)1,2.
Why CD23 Matters in Allergies
In allergic disorders, such as asthma or rhinitis, CD23 is a regulatory center for IgE activity. Not only does it stimulate IgE synthesis but it also allows IgE-bound allergens to be delivered to T-helper (T_H2) cells, which drive the allergic cascade. The outcome includes symptoms such as airway swelling, increased mucus production, and respiratory failure. By blocking CD23, we might be able to stop these harmful mechanisms and lessen the severity of allergies.
CD23's Role in CLL
In CLL, CD23 is overexpressed in cancerous B cells, making them grow and resist therapy. Attacking CD23 is a new way to break down these protective defenses and start destroying cancer cells. Gomiliximab takes advantage of this opportunity, delivering an individualized solution to this difficult disease.
How Gomiliximab Works
Gomiliximab's action is fast and aggressive. It targets only CD23 on the surface of the target cells and has several beneficial effects.
- Suppressing IgE Production
Probably Gomiliximab's most significant effect is its reduction of IgE levels. Cross-linking CD23 shuts down processes that induce IgE production. The studies have indicated that, in just one dose, a marked decline in serum IgE could occur for weeks. In patients with asthma or other IgE-related allergies, this may translate into fewer flare-ups and improved symptom control.
- Disrupting Antigen Presentation
By inhibiting CD23, Gomiliximab keeps immune cells from presenting allergens to T_H2 cells. This stops the allergic reaction at its most critical point and minimizes inflammation and other downstream effects. It's like shutting off the electrical supply to a factory assembly line—without it, the immune system cannot overreact to allergens.
- Inducing Cancer Cell Death
In CLL, Gomiliximab doesn't just regulate the immune system. It directly incites apoptosis (programmed cell death) in CD23-positive cancer cells. It's especially useful for patients with drug-resistant CLL because it gives them a lifeline where conventional therapies cannot.
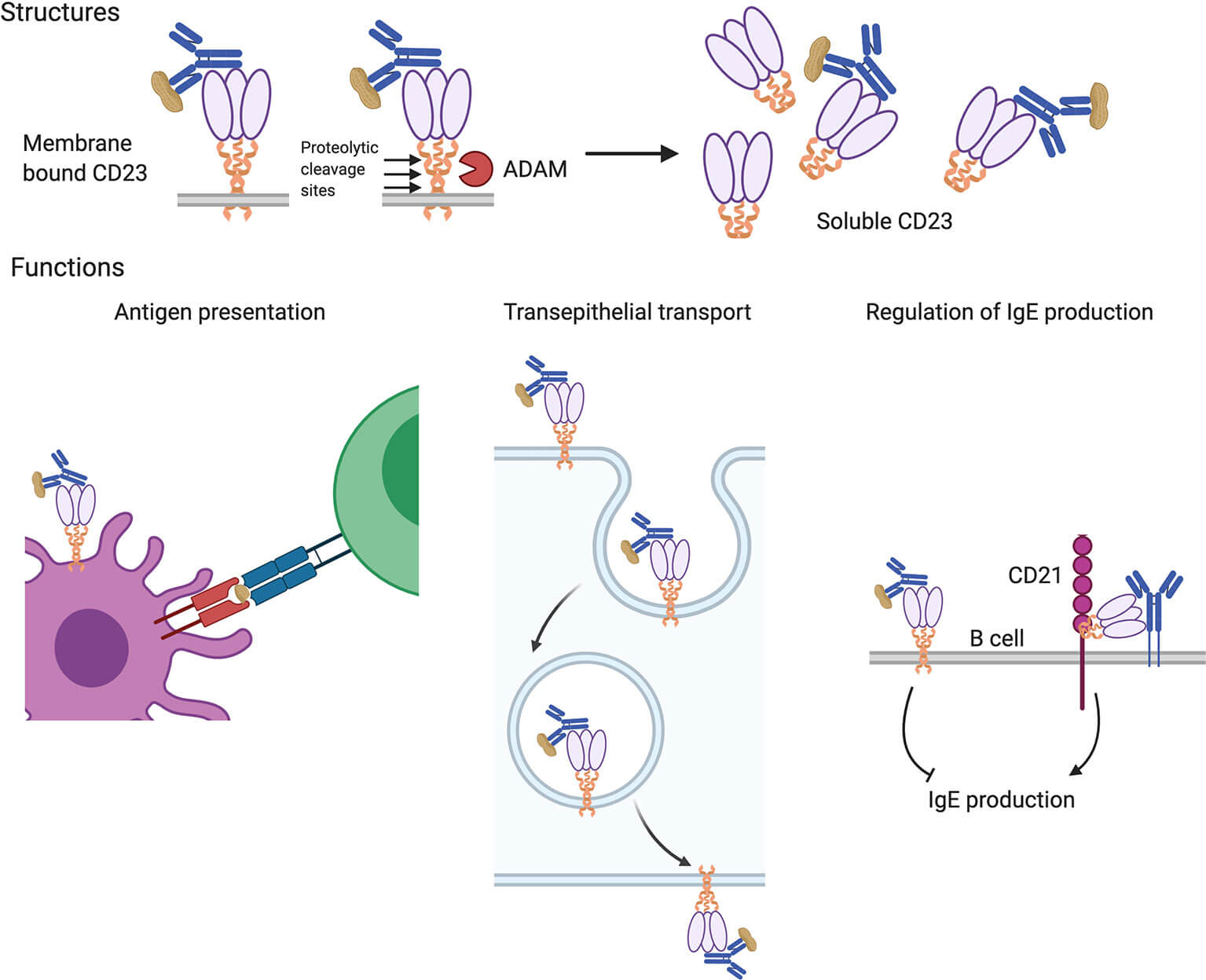 Figure 2. Structures and Functions of the Low-affinity IgE Receptor, CD233.
Figure 2. Structures and Functions of the Low-affinity IgE Receptor, CD233.
The Clinical Applications of Gomiliximab
- Allergic Asthma
Millions of people worldwide suffer from asthma, and IgE is at the center of their disease. Gomiliximab has been tested in Phase I asthma trials, and it proved safe and effective at reducing IgE. Single-dose therapy didn't improve lung function measures such as FEV1, but it has paved the way for repeated dose studies. This would offer a novel option for those suffering from asthma, particularly those who have extreme or intractable symptoms.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
By inhibiting CD23, Gomiliximab keeps immune cells from presenting allergens to T_H2 cells. This stops the allergic reaction at its most critical point and minimizes inflammation and other downstream effects. It's like shutting off the electrical supply to a factory assembly line – without it, the immune system cannot overreact to allergens.
- Broader Allergic Conditions
Gomiliximab's versatility goes beyond asthma. It also suppresses IgE-driven responses, making it a potential therapy for allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, and possibly food allergies. Such applications remain under development, but the science behind them is persuasive.
Clinical Projects of Gomiliximab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Start Date |
| NCT00103558 | Lumiliximab in Combination With FCR in Subjects With Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Completed | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | 2005-02-11 |
| NCT00046488 | Safety and Efficacy of IDEC-152 in the Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Completed | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | 2002-10-02 |
| NCT00391066 | Lumiliximab With Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, and Rituximab (FCR) Versus FCR Alone in Subjects With Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | Terminated | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | 2006-10-23 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=LumiliximabApproved Drugs of Gomiliximab**
What We Provide
Anti-Human CD23 Recombinant Antibody (Gomiliximab)
We provide high-quality gomiliximab for use in WB, Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC and most other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- primate
- Derivation
- Chimeric (primate/human)
- Type
- IgG1 - kappa
- Specificity
- Tested positive against native human antigen.
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in WB, Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 357613-86-6
- Generic Name
- Gomiliximab
- UNII
- 8Z13S29R5A
- UniProt Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P06734/entry#structure)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0] without modification.
- Kanagaratham, Cynthia, et al. "IgE and IgG antibodies as regulators of mast cell and basophil functions in food allergy." Frontiers in immunology 11 (2020): 603050. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



