Moxetumomab Pasudotox Overview
Introduction of Moxetumomab Pasudotox
Moxetumomab pasudotox (CAT-8015, HA22), an investigational targeted cancer therapy, is a recombinant immunotoxin composed of the Fv fragment of an anti-CD22 monoclonal antibody (mAb) fused to a 38 kDa fragment of Pseudomonas exotoxin A, called PE38. Moxetumomab pasudotox binds to CD22 and is internalized and processed. The released catalytic domain of the exotoxin inhibits protein translation leading to cell death. Moxetumomab pasudotox is an improved more active form of a predecessor recombinant immunotoxin BL22 (also called CAT-3888), which produced complete remissions (CRs) in relapsed/refractory hairy cell leukemia (HCL) but had < 20% response rate in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), diseases in which the leukemic cells contain much lower numbers of CD22 target sites. Currently, moxetumomab pasudotox is being investigated in patients for the treatment of CD22-expressing B-cell malignancies, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) and leukemia. In a multicenter Phase 1 study in adult patients with relapsed or refractory HCL, moxetumomab pasudotox exhibited substantial antitumor activities with an observed objective response rate of 86%. Besides additional testing in HCL, moxetumomab pasudotox is being evaluated in phase I trials in patients with CLL, B-cell lymphomas, and childhood ALL. Moreover, protein engineering has been used to increase its activity and to decrease non-specific side effects and remove B cell epitopes.
Mechanism of Action of Moxetumomab Pasudotox
CD22, a sialic acid binding immunoglobulin-like lectin (siglec), which inhibits B-cell receptor calcium signaling, is expressed on many B-cell malignancies, including HCL, CLL, B-cell NHL, and ALL. Moxetumomab pasudotox (CAT-8015) is a second generation, higher affinity anti-CD22 immunotoxin made through targeted mutations in the hotspot region of the complimentarity determining region (CDR)-3. Upon binding to CD22, moxetumomab pasudotox is internalized and after processing, a portion of the toxin is transferred to the endoplasmic reticulum and translocated into the cytosol. Here the toxin PE38 catalyses the ADP-ribosylation and inactivation of elongation factor-2, resulting in inhibition of protein synthesis and cell death.
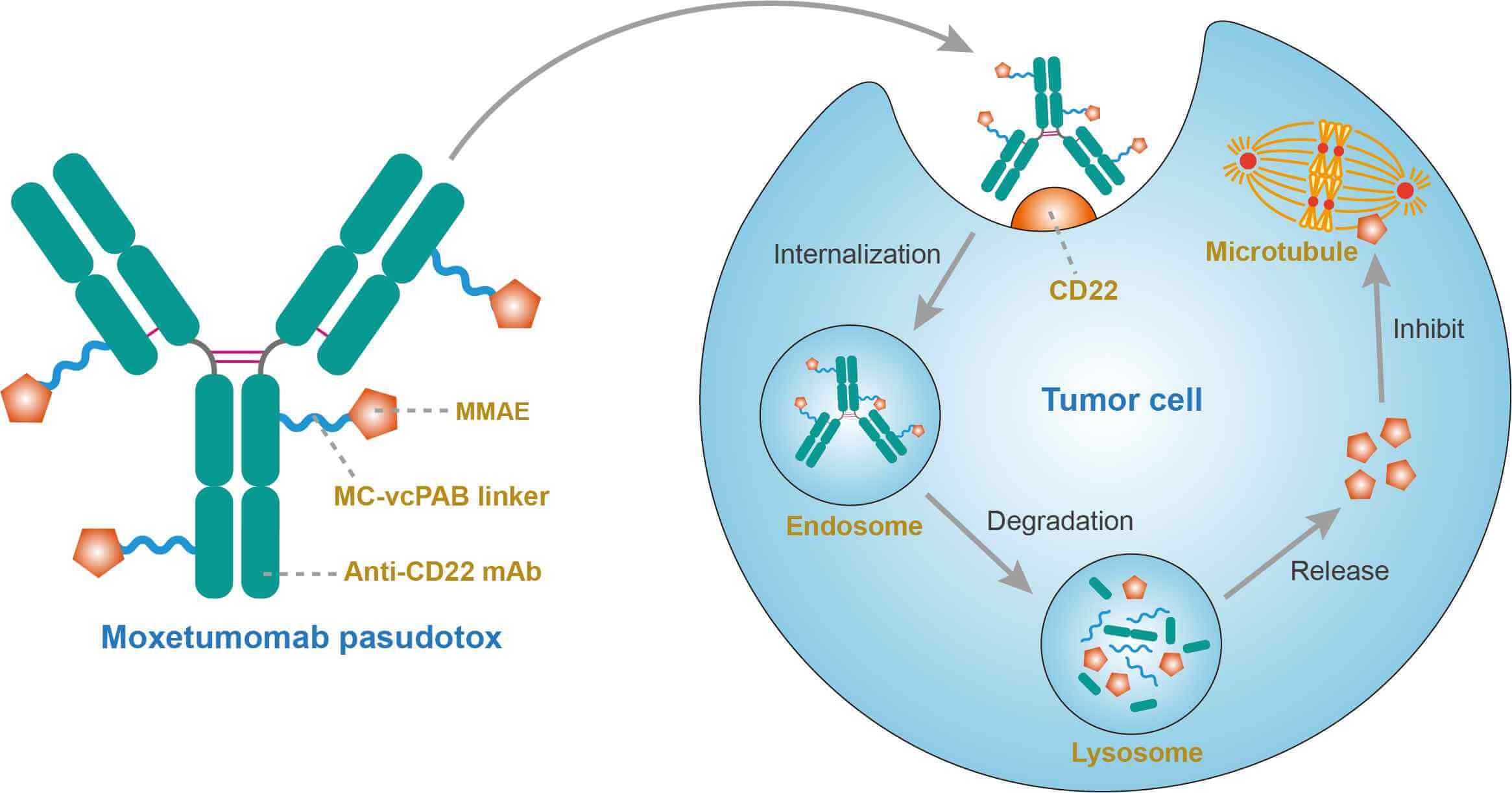 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Moxetumomab Pasudotox
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Moxetumomab Pasudotox
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



