Pritoxaximab Overview
Introduction of Pritoxaximab
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) are a significant public health threat worldwide, causing illnesses ranging from mild enteritis to severe complications such as hemolytic-uremic syndrome (HUS). Among the toxins produced by these bacteria, Shiga toxin 1 (Stx1) is particularly notorious for its association with severe clinical outcomes. It is composed of an active A subunit (32 kDa) and five receptor-binding B subunits (7.7 kDa each), with a total molecular weight of approximately 70 kDa. The A subunit is enzymatically active and responsible for the toxic effect by catalyzing the depurination of a conserved adenine residue of the 28S rRNA, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis. The B subunits are responsible for binding to host cell surface receptors like globotriaosylceramide (Gb3), facilitating the internalization of the toxin. The process of Stx1 migration begins with its binding to Gb3 receptors on host cells via B subunits, resulting in internalization. Once internalized, the toxin is transported retrograde to the Golgi apparatus and then to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) where the A1 subunit is cleaved and released into the cytosol, eventually leading to cell death.
Pritoxaximab is a recombinant monoclonal antibody specifically designed to target the B subunit of Stx1. By selectively binding to the B subunit, it neutralizes the toxin's activity and inhibits its interaction with the Gb3 receptor, thus restraining the internalization and toxicity of the toxin. One of the primary applications of pritoxaximab is to prevent immunocompromised patients from developing hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a high-risk disease induced by STEC infection. Early administration of pritoxaximab has shown potential in neutralizing the toxin before it exerts pathological effects during STEC infection, demonstrating promising therapeutic efficacy in preventing the development of HUS.
Biological and Chemical Properties of Pritoxaximab
Related Protein Structure
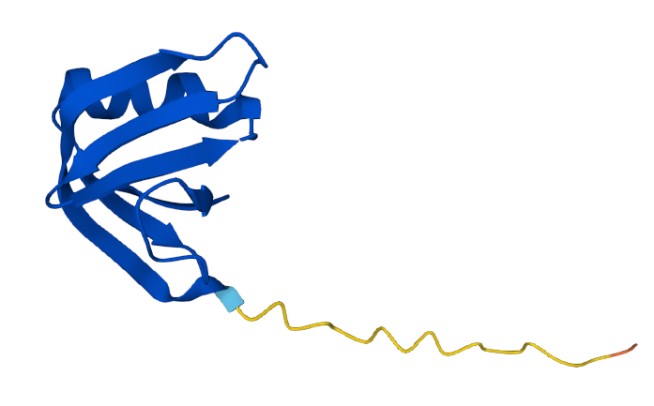 Figure 1. The Structure of Human SLT-I B Subunit (UniProt)1,2
Figure 1. The Structure of Human SLT-I B Subunit (UniProt)1,2
Protein Average Weight
The average weight of the protein is approximately 145.88 kDa.
The Mechanism of Pritoxaximab Action
The B subunit of Stx1 is a pentamer that binds to Gb3 receptors on host cells, allowing the toxin's enzymatic A subunit to enter cells and exert its toxic effect. Structurally, pritoxaximab is developed with a binding site specific to the B subunit of Stx1. By specifically binding to this subunit, pritoxaximab effectively blocks this critical initial binding step. Upon administration, pritoxaximab circulates through the bloodstream and binds to free Stx1-B subunits. This binding is highly specific with a strong affinity, which means that even small amounts of the antibody can neutralize significant quantities of the toxin. By attaching to the B subunit, pritoxaximab sterically hinders the toxin from interacting with Gb3 receptors on the surface of target cells. This blockade prevents the toxin's internalization into the host cells, thereby circumventing the potentially lethal pathway initiated by the A subunit. As a result, the toxin cannot enter the host cell, preventing cytotoxic effects, such as inhibition of protein synthesis related to cell death. Finally, the antibody-toxin complexes are usually cleared by the reticuloendothelial system, primarily the liver and spleen where they are phagocytosed and degraded. This efficient clearance minimizes the body's exposure to harmful toxins and reduces the severity of clinical symptoms associated with STEC infections.
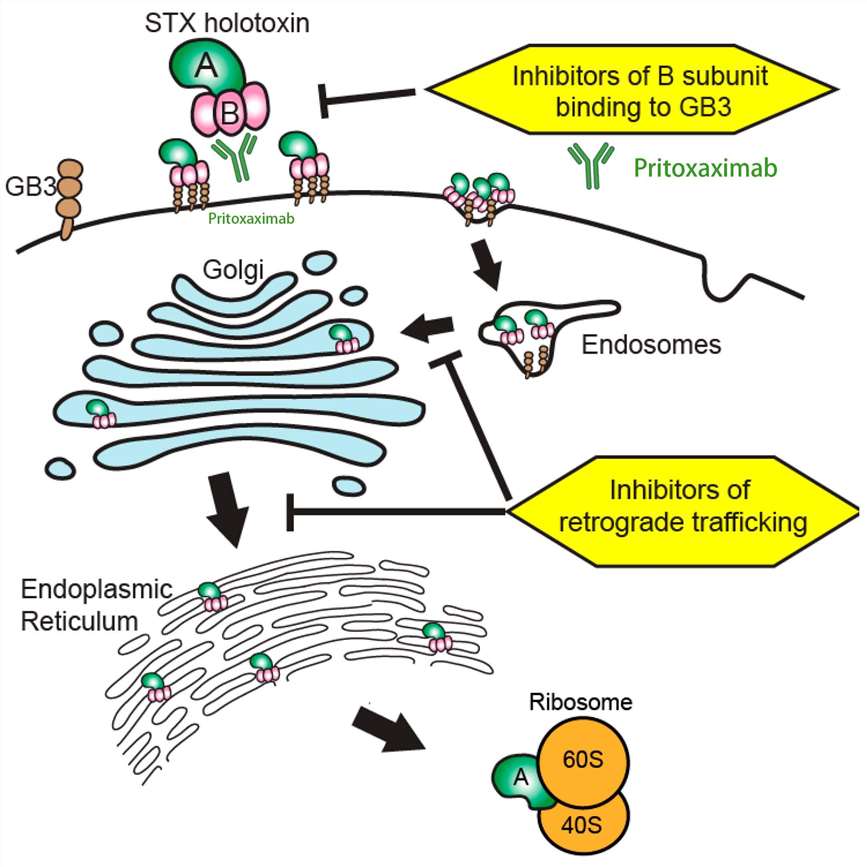 Figure 2. The Mechanism of Pritoxaximab Action3,4
Figure 2. The Mechanism of Pritoxaximab Action3,4
What We Provide
Anti-Shiga Toxin 1 B Subunit Recombinant Antibody (Pritoxaximab)
We provide high-quality pritoxaximab suitable for use in Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC, IHC, and other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, and diagnostic use, therapeutic application, or any in vivo human use are not advised.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Derivation
- Chimeric (Human/Mouse)
- Type
- IgG1 - kappa
- Species Reactivity
- E. coli
- Applications
- Suitable for use in Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC, IHC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 1351470-16-0
- Generic Name
- Pritoxaximab
- Related Disease
- STEC (Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli or E. coli serotype O121) infection causing diarrhea and HUS (hemolytic-uremic syndrome)
- Uniprot Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q47641/entry#structure)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0]. It was not modified and the titles was " The Structure of Human SLT-I B Subunit (UniProt)".
- Hall, Gregory et al. "Shiga Toxin Therapeutics: Beyond Neutralization." Toxins vol. 9,9 291. 19 Sep. 2017.
- Images retrieved from Figure 1 "Shiga Toxin Therapeutics: Beyond Neutralization." Hall, Gregory, 2017, used under [CC BY 4.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). The image was modified by adding 2 texts "Pritoxaximab" and 2 Y-shaped antibody pictures colored with green, and the title was changed to "The Mechanism of Pritoxaximab Action".
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

