Rosmantuzumab Overview
Introduction of Rosmantuzumab
Rosmantuzumab, also known as OMP-131R10, is a specially engineered monoclonal antibody designed to target the R-spondin 3 (RSPO3) protein. RSPO3, a member of the R-spondin family, plays a significant role in the modulation of the Wnt signaling pathways. By binding to RSPO3, rosmantuzumab inhibits its interaction with corresponding receptors such as LGR4, LGR5, and LGR6, thereby curtailing the aberrant activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway—a processs extensively implicated in various cancers. Initially developed by OncoMed Pharmaceuticals, rosmantuzumab is currently being investigated for its potential in treating cancers associated with abnormal Wnt signaling, particularly colorectal cancer and other solid tumors.
Biological and Chemical Properties of Rosmantuzumab
Protein Structure
 Figure 1. The Structure of Human R-spondin-3 (UniProt)1,2
Figure 1. The Structure of Human R-spondin-3 (UniProt)1,2
Protein Chemical Formula
C6456H9954N1714O2048S46
The Mechanism of Rosmantuzumab Action
RSPO3 is one of four members of the R-spondin family, a group of secreted proteins crucial for enhancing Wnt signaling. RSPO3 interacts with leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptors (LGRs) such as LGR4, LGR5, and LGR6. This interaction activates both the canonical Wnt/β-catenin pathway and non-canonical pathways. Normally, RSPO3 stabilizes the Frizzled/LRP5/6 receptor complexes on the cell surface, facilitating the accumulation and translocation of β-catenin to the nucleus. β-catenin then activates the transcription of Wnt target genes involved in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and stem cell renewal. In disease states, particularly in oncology, the overexpression or dysregulation of RSPO3 is linked to the aberrant activation of the Wnt signaling pathway. Continuous activation of this pathway results in uncontrolled cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, and tumorigenesis. Enhanced RSPO3 expression has been identified in colorectal, ovarian, and other solid tumors, making it a critical target for therapeutic intervention.
Rosmantuzumab exerts its anti-cancer effects by neutralizing RSPO3 activity. The antibody binds to RSPO3 with high specificity and affinity, preventing RSPO3 from interacting with its receptors, LGR4, LGR5, and LGR6. By sequestering RSPO3, rosmantuzumab inhibits the formation of the Frizzled/LRP5/6 receptor complex. This inhibition disrupts the downstream Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, blocking the translocation of β-catenin to the nucleus and reducing the transcription of Wnt target genes. Consequently, this blockade leads to decreased cellular proliferation.
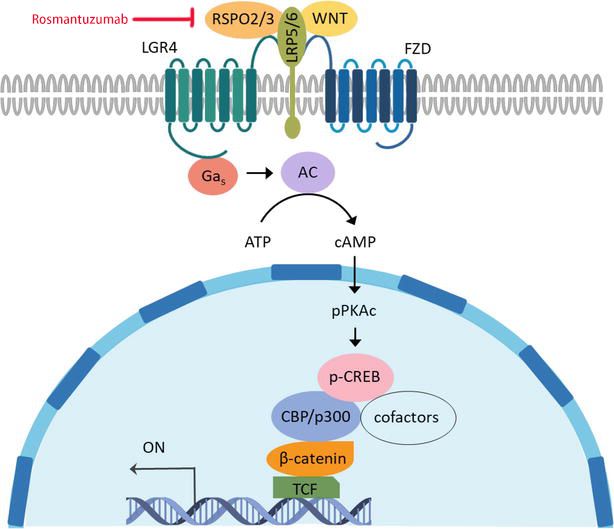 Figure 2. WNT/β-catenin Signaling Pathway and The Mechanism of Rosmantuzumab Action3,4
Figure 2. WNT/β-catenin Signaling Pathway and The Mechanism of Rosmantuzumab Action3,4
Clinical Projects of Rosmantuzumab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT02482441 | A Phase 1a/b Dose Escalation Study of the Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of OMP-131R10 | COMPLETED |
Advanced Relapsed Tumors Refractory Solid Tumors |
OncoMed Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 2015-07-16 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=OMP-131R10
What We Provide
Anti-Human RSPO3 Recombinant Antibody (Rosmantuzumab)
We provide high-quality rosmantuzumab for use in ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, and FuncS. The product is intended for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human applications.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Human
- Derivation
- Humanized
- Type
- IgG1, κ
- Specificity
- Human RSPO3
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, FuncS
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- CAS
- 1684393-04-1
- Generic Name
- Rosmantuzumab
- UNII
- VD026R6TCI
- Related Disease
- Advanced Relapsed Tumor, Refractory Solid Tumors

Figure 1 Anti-Human RSPO3 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-449CQ) in SDS-PAGE
Lane 1: 2 μg, Non-Reducing mAb Lane 2: 2 μg, Reducing mAb
- Uniprot Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q9BXY4/entry#function)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0]. It was not modified and the title was "The Structure of Human R-spondin-3".
- Yang, Jonason, et al. "Self-Renewal Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells." Acute Leukemias, IntechOpen, 2021.
- Images retrieved from Figure 4 "Self-Renewal Pathways in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells." Yang, Jonason, 2021, used under [CC BY 3.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0). The image was modified by adding the text "Rosmantuzumab" and the title was changed to "WNT/β-catenin Signaling Pathway and The Mechanism of Rosmantuzumab Action".
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

