Setoxaximab Overview
Introduction of Setoxaximab
Setoxaximab is a recombinant monoclonal antibody specifically engineered to recognize and bind to the Stx2A subunit of the Shiga toxin produced by pathogenic E. coli strains. Shiga toxins, named after the Japanese bacteriologist Kiyoshi Shiga, are virulence factors created by specific strains of E. coli inducing severe disease in humans. The primary diseases associated with Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) infections include hemorrhagic colitis (HC). Structurally, Shiga toxins are composed of two principal subtypes—Stx1 and Stx2. Stx2A, forming the active part of the Stx2 toxin with special RNA N-glycosidase activity. This enzymatic vitality can help cleave a specific adenine nucleotide from the 28S rRNA in the 60S ribosomal subunit and effectively halt elongation factor-1 dependent protein synthesis, resulting in cellular apoptosis or necrosis. In infected individuals, Shiga toxins are released following the bacterial cell lysis and spread systemically and target various cells, including endothelial cells in the gut and kidneys. The interaction with these cells leads to microvascular injury, triggering inflammation, thrombosis, and a cascade of events resulting in conditions like HUS. The kidney is particularly susceptible due to its high expression of the toxin's receptor, globotriaosylceramide (Gb3).
Biological and Chemical Properties of Setoxaximab
Protein Average Weight
The average weight of the protein is approximately 148,000 Da.
The Mechanism of Action of Setoxaximab
Setoxaximab represents a significant advancement in the targeted therapy of Shiga toxin-mediated diseases. Focused on neutralizing the Stx2A subunit, its mechanism of action offers a direct approach to preventing the severe complications associated with STEC infections. In the absence of setoxaximab, the Stx2A subunit binds to the Gb3 receptor, facilitates endocytosis, and undergoes transport to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Within the ER, the A subunit translocates to the cytoplasm, where it exerts its ribosome-inactivating function by cleaving adenine from the 28S rRNA. Upon administration, setoxaximab circulates and identifies free Stx2A toxins to form the specific antibody-toxin complexes, which effectively prevents the interaction between the toxin and the Gb3 receptor on host cells. Then the newly-formed antibody-Stx2A complexes taking place of the Stx2A-Gb3 conjugate fail to be internalized by endothelial cells, thereby inhibiting the ribosome-inactivating activity. Additionally, the formation of setoxaximab-toxin complexes could also facilitate the clearance of the toxin via immune pathways, such as phagocytosis by macrophages.
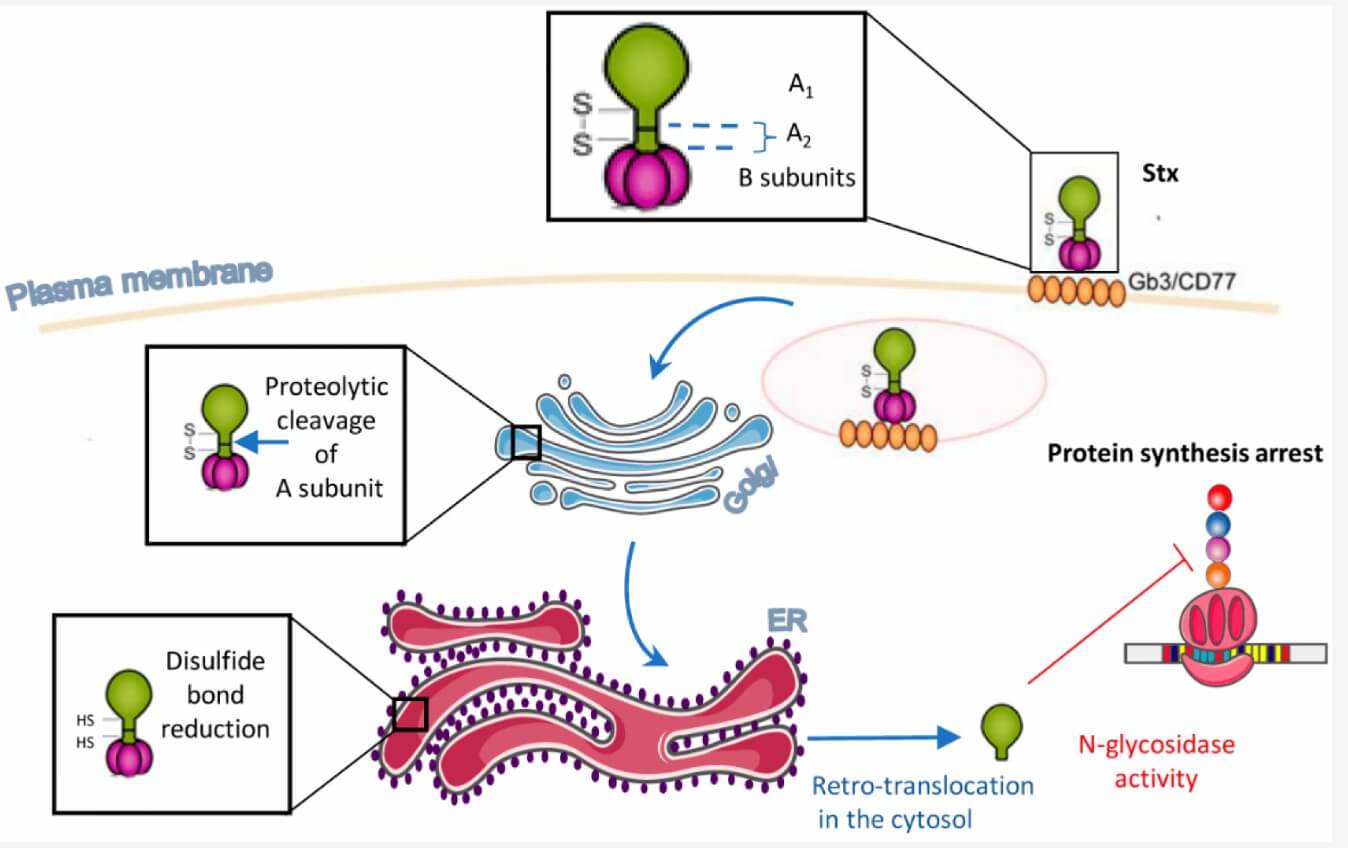 Figure 1. The Mechanism of Action of Setoxaximab1,2
Figure 1. The Mechanism of Action of Setoxaximab1,2
Clinical Applications of Setoxaximab
Firstly, setoxaximab could be utilized to prevent serious complications in patients diagnosed with STEC infections by neutralizing Stx2A before systemic spread and organ damage occur. Early administration could potentially reduce the risk of progressing to HUS. Apart from that, setoxaximab could halt the progression of the disease by neutralizing circulating Stx2A in patients exhibiting early signs of HUS, thereby preventing further endothelial cell damage and kidney dysfunction. Moreover, setoxaximab could also be part of combination therapies with other antimicrobial agents aimed at eliminating the bacterial source while neutralizing the toxin.
What We Provide
Anti-E. Coli Stx2A Recombinant Antibody (Setoxaximab)
We offer top-notch setoxaximab for use in FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF, ICC, and most other immunological methods. The product is designed for lab research use only, and is not suggested for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human applications.
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Derivation
- Mouse
- Type
- IgG1 - kappa
- Specificity
- shiga toxin type 2 (shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC), stx2, Stx2, Stx-2, Shiga-like toxin 2, SLT-2, SLT-II) A subunit [Escherichia coli]
- Species Reactivity
- E. coli
- Applications
- Suitable for use in FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF, ICC and most other immunological methods.
- CAS
- 1351470-17-1
- Generic Name
- setoxaximab
- Related Disease
- STEC (Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli or E. coli serotype O121) infection causing diarrhea and HUS (hemolytic-uremic syndrome)
- Robert, Aude et al. "Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools." Toxins vol. 13,10 690. 28 Sep. 2021.
- Images retrieved from Figure 1 "Shiga Toxins as Antitumor Tools." Robert, Aude, 2021, used under CC BY 4.0. The image was modified by adding the text "Setoxaximab" and the title was changed to " The Mechanism of Action of Setoxaximab".
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



