Volociximab Overview
Introduction of Volociximab
Volociximab, also known as M200 and Eos 200-4, is a first-in-class high-affinity IgG4 chimeric (82% human, 18% murine) monoclonal antibody (mAb). It can bind to and inhibit the activity of α5β1 integrin, thereby inhibiting endothelial cell-cell interactions, endothelial cell-matrix interactions, and angiogenesis. In addition, volociximab is developed for the treatment of a variety of advanced solid tumors. It is thought to reduce metastases and is investigated for use/treatment in solid tumors, renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, pancreatic cancer, lung cancer, and ovarian cancer.
Mechanism of Action of Volociximab
Integrins are a superfamily of widely expressed transmembrane glycoprotein receptors for extracellular matrix ligands, such as fibronectin, vitronectin, laminin, collagens, and other plasma membrane proteins, and function in the regulation of a broad variety of cellular processes, including embryogenesis, inflammation, bone metabolism, apoptosis, cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and tumor metastasis. Integrins exist as noncovalent heterodimers comprising α and β subunits. Receptor diversity, function, and versatility in ligand binding is determined by the specific pairing of α and β subunits. The cytoplasmic tail of the β subunit links to the actin cytoskeleton and components of the focal adhesion plaque. The interaction with the focal adhesion plaque can lead to signaling, through different pathways, to influence cell survival, growth, and motility. Consequently, all of these protein associations allow cells to sense and respond to their extracellular environment. Endothelial cell expression of the α5β1 integrin and the ligand fibronectin are both up-regulated during tumor angiogenesis. The sites of the α5β1 integrin increase in expression and are more accessible in the vasculature during angiogenesis and tumor growth, which is in contrast to normal tissue vasculature. Disruption of α5β1 integrin binding to fibronectin results in the inhibition of angiogenesis and the induction of apoptosis of activated endothelial cells. Volociximab is a high-affinity IgG4 chimeric monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to α5β1 integrin and inhibits the functional activity of α5β1 integrin. Previously, it has been proved that this antibody elicits cell death in dividing endothelial cells, inhibits angiogenesis in a cynomolgus monkey model of choroidal neovascularization and slows tumor growth in a rabbit VX2 carcinoma model.
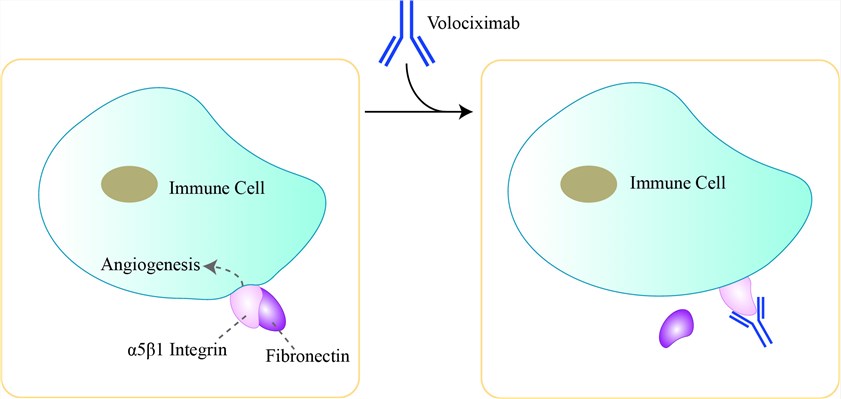 Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Volociximab
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Volociximab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

