Xentuzumab Overview
Introduction of Xentuzumab
Xentuzumab (BI 836845) is a humanised IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that targets both insulin-like growth factor (IGF) ligands, IGF-1 and IGF-2, thereby inhibiting downstream signalling. Clinical trials to evaluate xentuzumab as a treatment for patients with solid tumours including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), breast cancer and prostate cancer are being conducted.
Mechanism of Action of Xentuzumab
The insulin family of growth factors is an evolutionally conserved system which plays a crucial role in the growth and development of many tissues and the regulation of overall growth and metabolism. This system comprises three receptors [insulin receptor (IR), IGF-1 receptor (IGF-1R), and IGF-2/mannose 6-phosphate receptor (M-6-PR)], three ligands (insulin, IGF-1, and IGF-2), and six known types of circulating IGF-binding proteins (IGFBP1-6). The IGF-1R is highly homologous to the IR.
The IGF-1R is a receptor tyrosine kinase with a structure of a heterotetrameric glycoprotein composed of two α and two β subunits, post-transcriptionally linked by disulfide bonds, which regulates cell survival and cell cycle progression via the PI3K/Akt and extracellular signal regulated kinase pathways through insulin receptor substrate-1to-4 (IRS-1to-4) and Src-homology collagen (Shc) adapter proteins. Phosphorylation of the IRS adapter molecules on one hand triggers activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway, whereas, on the other hand, the Shc adapter activates signaling by the Ras/Raf/MEK/Erk signaling pathway. IGF-IR seems to be expressed in most human cancers. The two IGF-1R ligands, IGF-1 and IGF-2, have been implicated in cancer initiation and progression.
In the past decades, a large amount of evidence has emphasized that IGF-1R play a key role in the transformation of cells, cancer cell proliferation, as well as in metastatic events, associated in various types of human cancers. It seems that inhibition of IGF-1R signaling can generate antineoplastic effects.
A number of monoclonal antibodies have been developed to target the receptor itself, which bind to the extracellular domains of the IGF-1R and block ligand binding. However, efficacy of anti-IGF-1R antibodies has been disappointing in clinical trials to date. Another therapeutic approach is to target the IGF-1 and IGF-2 ligands directly. Xentuzumab, a fully human mAb that neutralizes the activities of both IGF-1 and IGF-2, inhibits proliferative/anti-apoptotic signaling via IGF-1R.
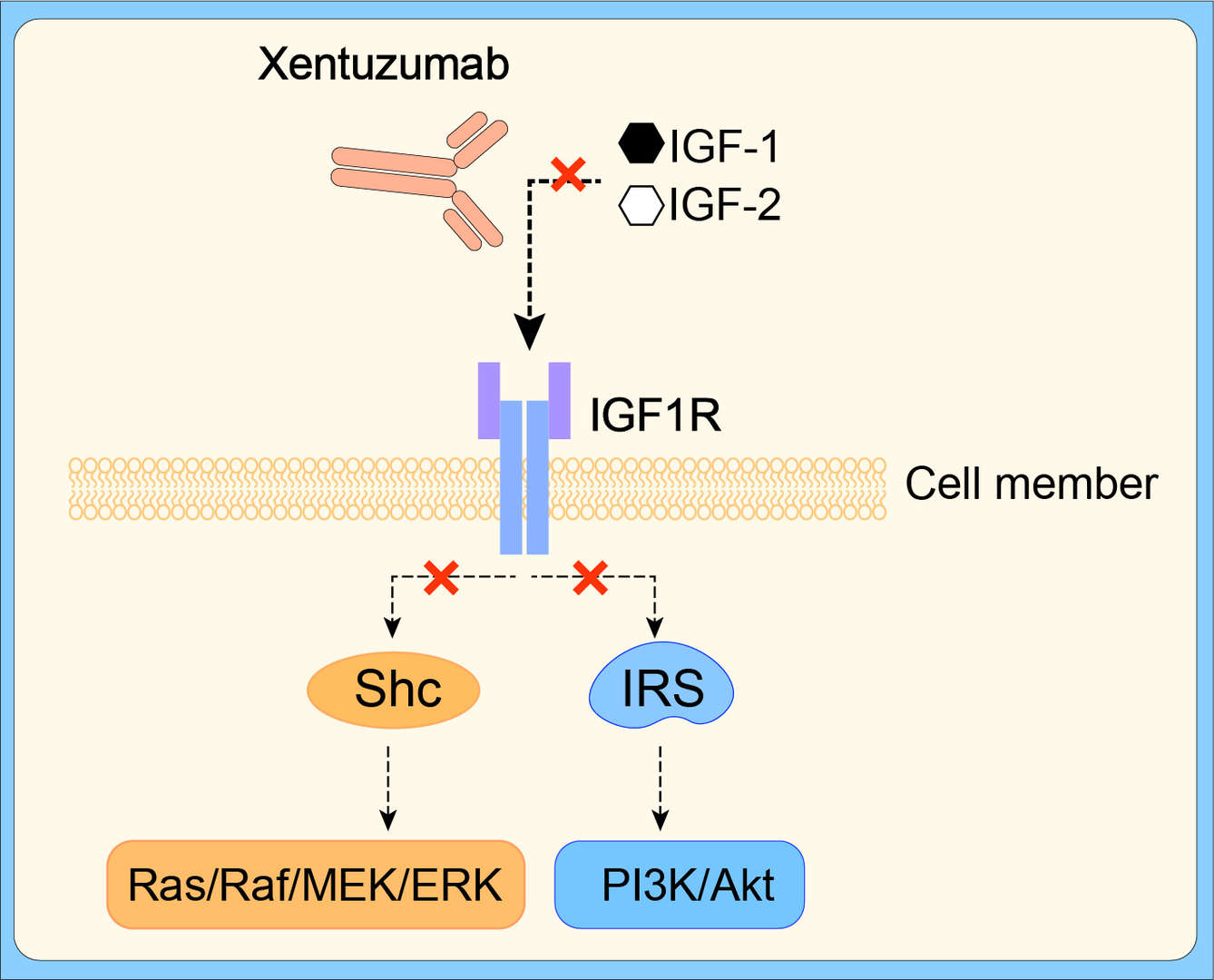 Figure 1 Mechanism of Action of Xentuzumab
Figure 1 Mechanism of Action of Xentuzumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



