Asthma Overview
About Asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Some symptoms, including episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath, may show asthma. This disease is commonly thought to be caused by the combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors mainly refer to the exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential factors include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Asthma is classified according to the frequency of symptoms, forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), and peak expiratory flow rate. It may also be classified as atopic or non-atopic, where atopy refers to a predisposition toward developing a type 1 hypersensitivity reaction. Asthma is a chronic disease and occurs in people of all ages. It is the most common chronic disease in children. Recently, asthma affects about 235 million people by 2017 in the world.
Main Signaling Pathways in Asthma
Diagnosis of Asthma
To diagnose asthma, there are several steps to confirm. Firstly, personal and medical history. Doctors will ask questions to understand patients’ symptoms and their causes. At the same time, to answer questions about patients’ family history, the medicines you take and your lifestyle. Secondly, the physical exam. Doctors will look at ears, eyes, nose, throat, skin, chest and lungs to confirm. Thirdly, lung function tests. Lung function tests are often done before and after inhaling a medicine known as a bronchodilator (brahn-ko-DIE-ah-lay-tor), which opens your airways. If your lung function improves a lot due to the bronchodilator, you probably have asthma. Subsequently, going through common lung function tests used to diagnose asthma, including spirometry, peak airflow, and FeNO tests (exhaled nitric oxide). Besides that, these also include a chest X-ray, acid reflux test, sinus X-rays or other specialized tests. At the same time, doctors may perform allergy tests because allergies can cause asthma. Especially for children under 5, diagnosing asthma is usually not given a breathing test. In fact, the doctor asks about certain signs and symptoms and prescribes a bronchodilator to check. If the bronchodilator helps reduce their symptoms, that means they may have asthma.
Targeted Therapy for Asthma
Treatments for asthma usually learn to recognize triggers firstly, and then taking steps to avoid them and tracking your breathing to make sure your daily asthma medications are keeping symptoms under control. Based on different types of asthma, there are different therapies for patients. For long-term asthma patients, long-term asthma control medications, generally taken daily, are the cornerstone of asthma treatment. These medications keep asthma under control on a day-to-day basis.
-
Types of long-term control medications include:
- Inhaled corticosteroids, such as fluticasone (Flonase, Flovent HFA), budesonide (Pulmicort Flexhaler, Rhinocort), flunisolide (Aerospan HFA), ciclesonide (Alvesco, Omnaris, Zetonna), beclomethasone (Qnasl, Qvar), mometasone (Asmanex) and fluticasone furoate (Arnuity Ellipta).
- Leukotriene modifiers, oral medications, including montelukast (Singulair), zafirlukast (Accolate) and zileuton (Zyflo). These drugs help relieve asthma symptoms for up to 24 hours.
- Long-acting beta agonists. These inhaled medications include salmeterol (Serevent) and formoterol (Foradil, Perforomist) and help open the airways.
- Combination inhalers, such as fluticasone-salmeterol (Advair Diskus), budesonide-formoterol (Symbicort) and formoterol-mometasone (Dulera).
- Theophylline is a daily pill that helps keep the airways open (bronchodilator) via relaxing the muscles around the airways.
-
Types of quick-relief medications include:
- Short-acting beta agonists, include albuterol (ProAir HFA, Ventolin HFA, others) and levalbuterol (Xopenex). These quick-relief bronchodilators act within minutes to quickly ease symptoms during an asthma attack.
- Ipratropium (Atrovent) acts immediately relax airways and makes easily breathe.
- Prednisone and methylprednisolone, which are oral and intravenous corticosteroids, relieve airway inflammation caused by severe asthma.
-
Allergy medications include:
- Allergy shots (immunotherapy). Over time, allergy shots gradually decrease the immune system reaction to specific allergens. Patients generally receive shots once a week for a few months, then once a month for a period of three to five years.
- Omalizumab (Xolair). This medication, given as an injection every two to four weeks, is specifically for people who have allergies and severe asthma. It acts by altering the immune system.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


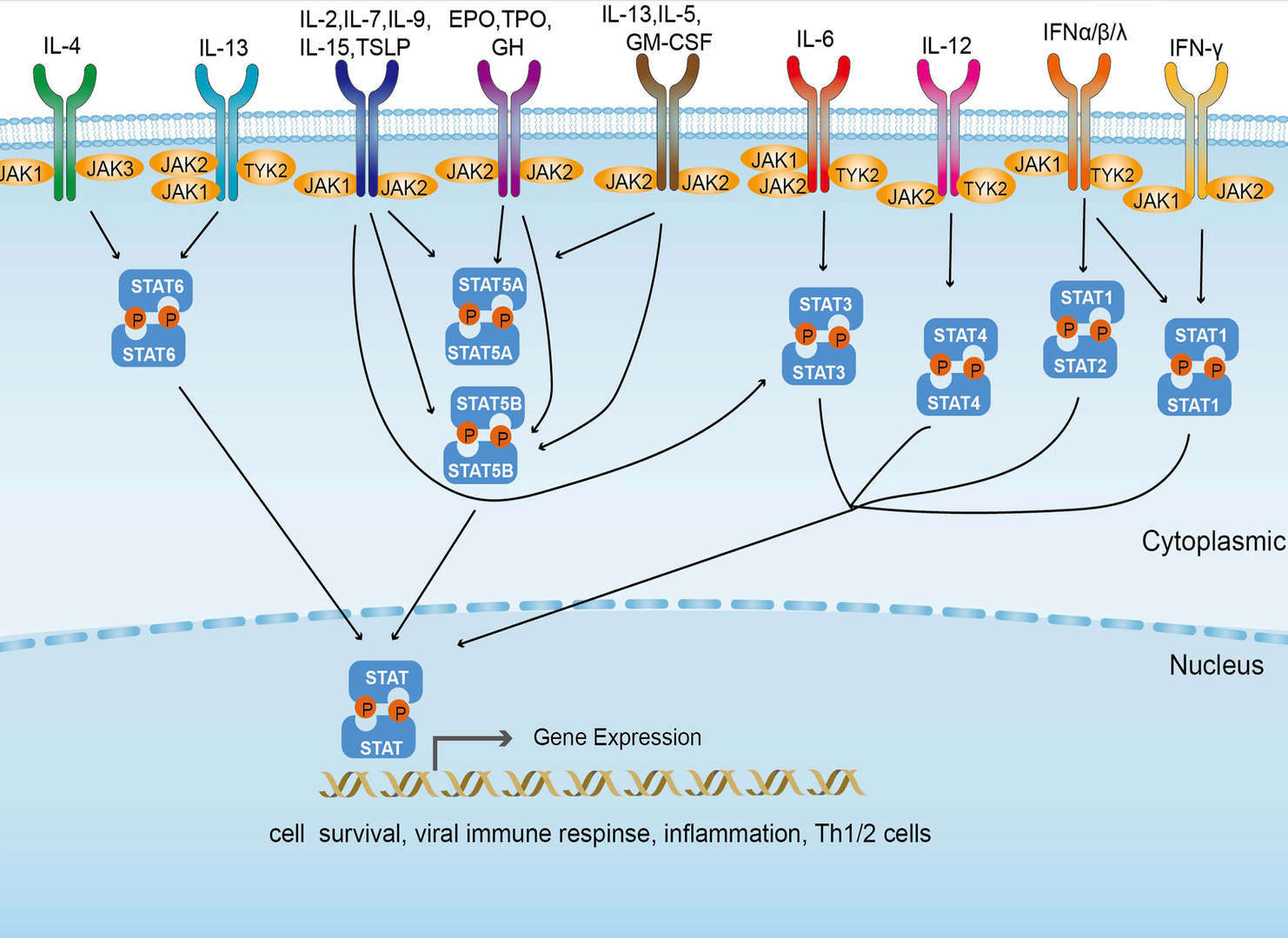 JAK-STAT signal pathway
JAK-STAT signal pathway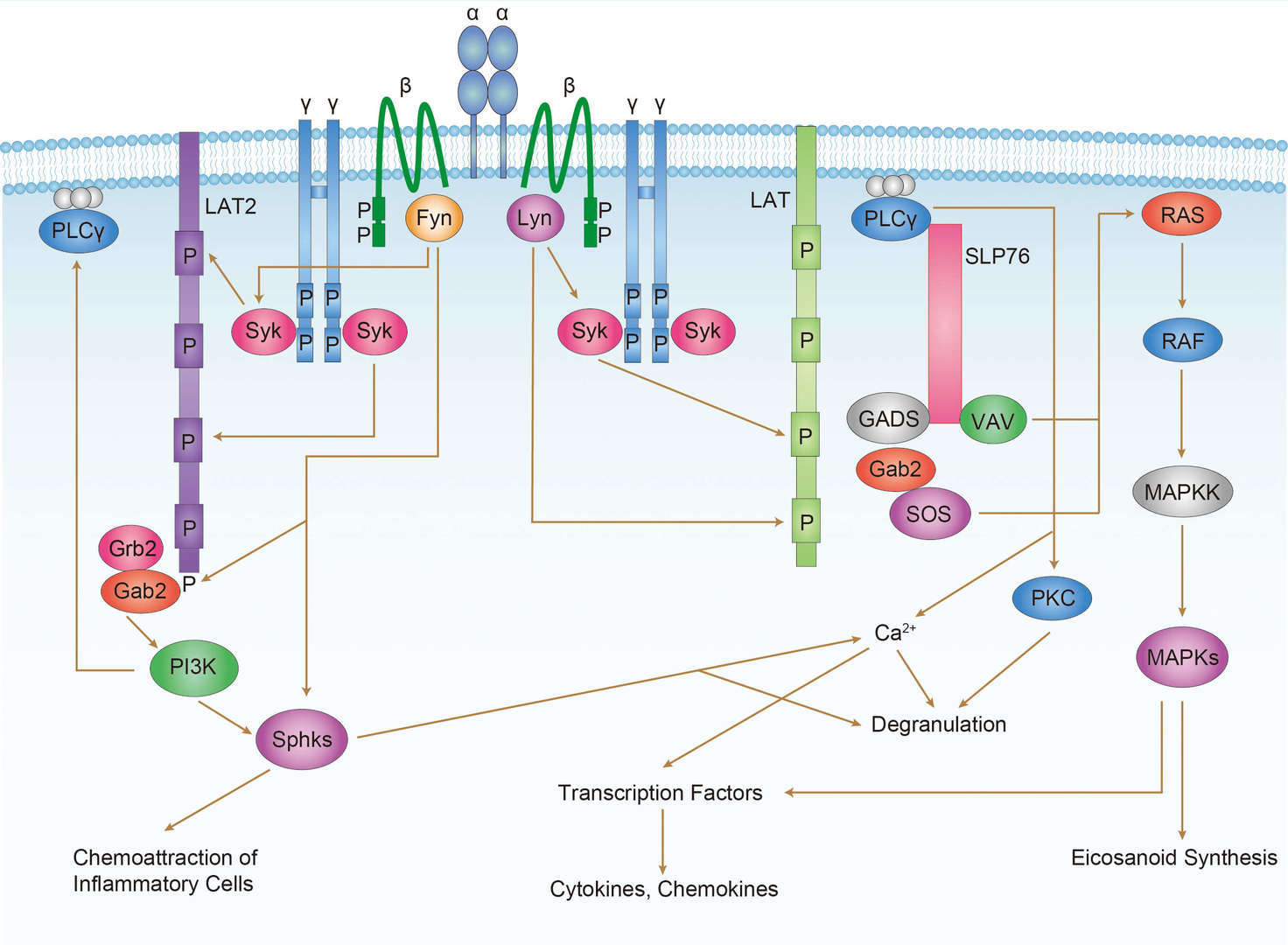 FcεRI signal pathway
FcεRI signal pathway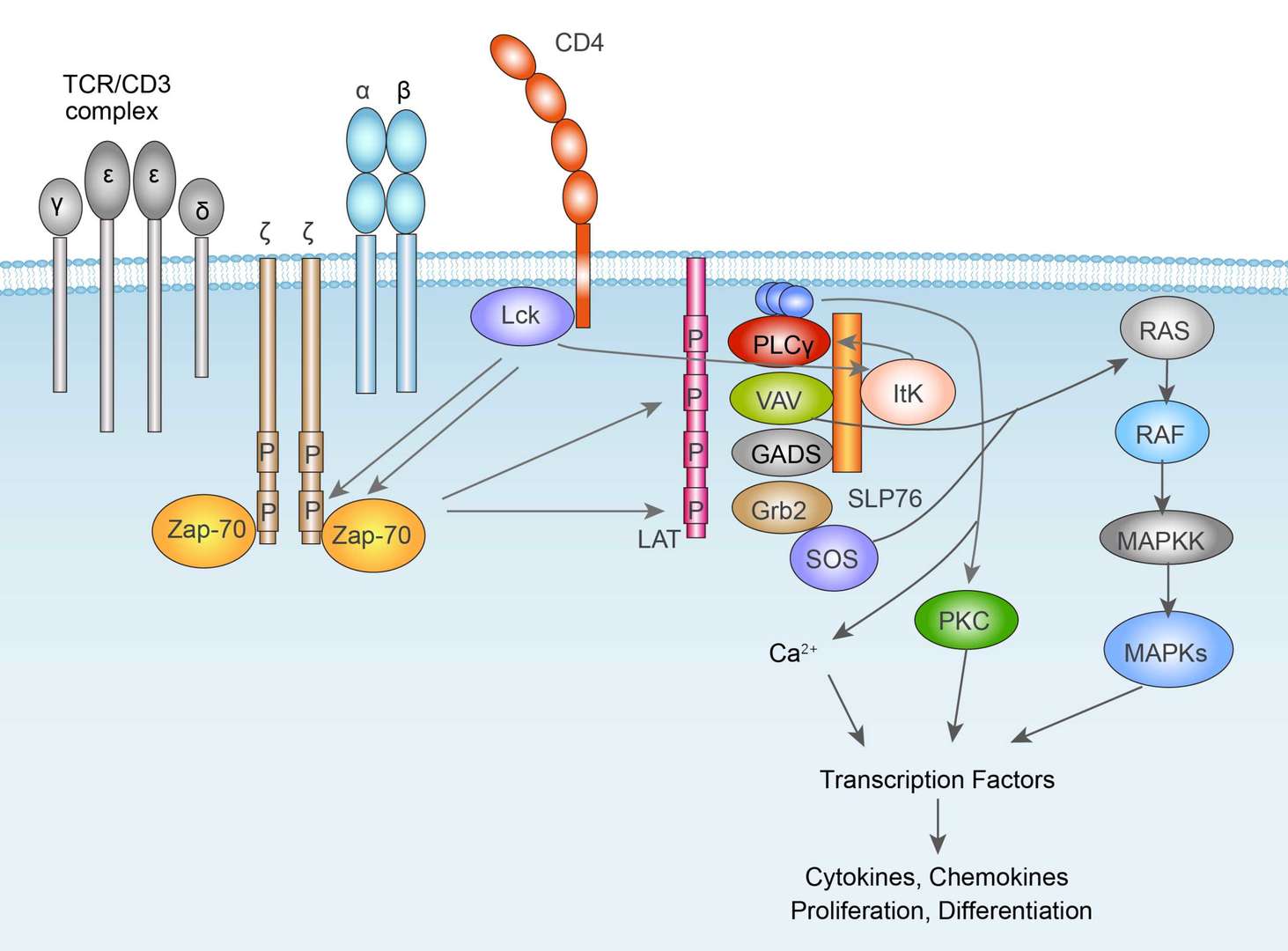 TCR signal pathway
TCR signal pathway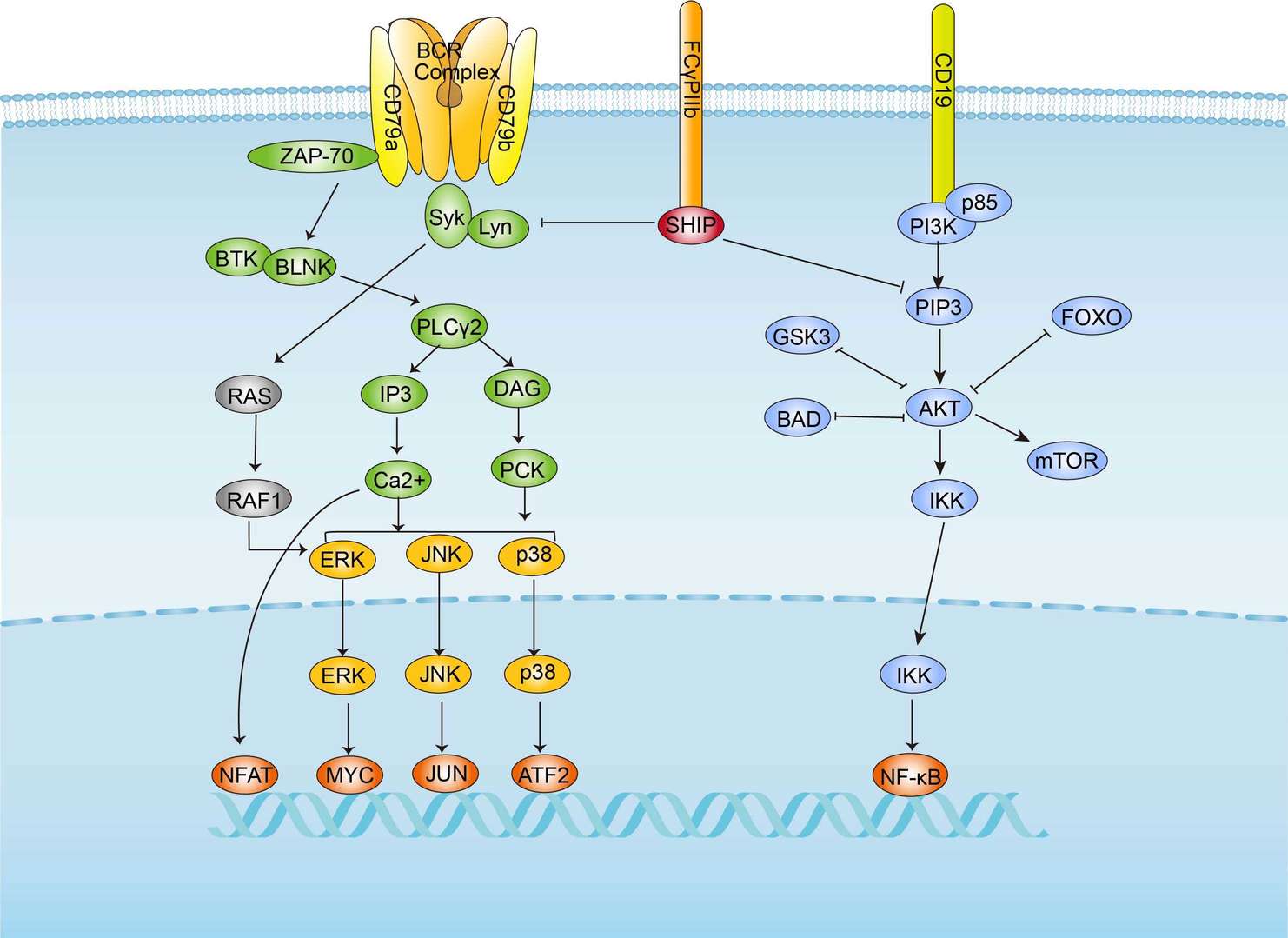 BCR signal pathway
BCR signal pathway