Lodelcizumab Overview
Introduction of Lodelcizumab
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) is responsible for lowering LDL-C levels. The presence of high LDL-C is a well-known risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) like atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Learning the role that PCSK9 plays in the metabolism of LDL-C led to the discovery of new therapeutics. lodelcizumab, also known as NVP-LGT-209, LGT-20, is a 100% human monoclonal antibody developed by Novartis Pharma AG that destroys PCSK9. Blocking the PCSK9's engagement with LDL receptors (LDLRs), lodelcizumab ensures that those receptors are re-expressed back on the surface of liver cells and this boosts the elimination of LDL-C from the blood. With its remarkable efficacy, favorable safety profile, and versatility in use to support patients of all ages, lodelcizumab is an innovative treatment for cholesterol management.
The Role of PCSK9 in LDL-C Metabolism
LDL Receptor Recycling and PCSK9 Function
LDL-C is mostly removed from the bloodstream by LDL receptors (LDLRs) on the surface of hepatocytes. LDLR binds to LDL and allows them to be internalized by endocytosis. LDL is destroyed in lysosomes after endocytosis, and LDLR returns to the cell surface to be recycled. This recycling process is vital for the regulation of LDL-C homeostasis.
The serine protease PCSK9 is key to this function because it binds to LDLR and directs it to be broken down at the lysosomes rather than recycled. Thus, increased PCSK9 activity reduces the LDLRs available on liver surfaces, disrupting LDL-C clearance and causing elevated plasma levels of LDL-C. Gain-of-function mutations in the PCSK9 gene cause this, while loss-of-function mutations reduce LDL-C and lower CVD risk.
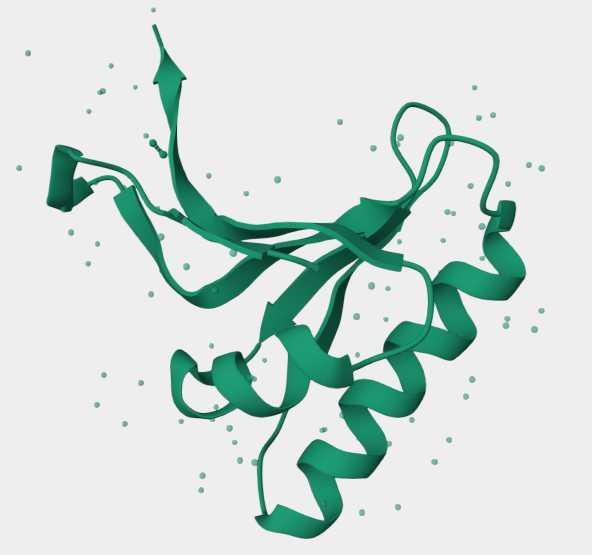 Figure 1. The Structure of Human PCSK91,2.
Figure 1. The Structure of Human PCSK91,2.
Why Target PCSK9?
Clinically, the significance of PCSK9 is to regulate the presence of LDLR. Classical LDL-C-lowering medications such as statins suppress cholesterol production and indirectly increase LDLR expression. But statins also activate PCSK9 expression, which can reduce their ability to lower LDL-C. This feedback loop highlights direct PCSK9 inhibitors as a second or third approach.
Therapeutic Significance of PCSK9 Inhibition
Lodelcizumab as a PCSK9 inhibitor is potentially very useful in sponging up the void of lipid-lowering medications. Statins and ezetimibe are the first-line treatments for high LDL-C, but they have their limits, with varying effectiveness and intolerance in certain patients. For patients with statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS) or familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), lodelcizumab can be a suitable alternative or complementary treatment.
Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase, an important cholesterol-suppressing enzyme, and lower LDL-C. But statins also promote the expression of PCSK9 and can ultimately slash their effects on LDL-C. By directly interacting with and inhibiting PCSK9, lodelcizumab provides an additive or synergistic effect when used in conjunction with statins by limiting the degradation of LDLRs and assisting the liver to eliminate LDL-C. This makes it especially useful for patients who require more LDL-C lowering in addition to statin therapy.
Lodelcizumab also offers a non-statin option for LDL-C inhibition for patients with statin-associated muscle symptoms (SAMS), an unpleasant side effect of statin therapy. So it is an invaluable therapy for those who are unable to take statins due to muscle aches or weakness, and a non-myopathic alternative that is safe and effective.
Lodelcizumab has also been successfully administered to patients with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), a genetic disorder caused by LDLR or associated genes. These mutations lead to very high LDL-C that is resistant to standard therapies. Lodelcizumab has been successfully used to reduce LDL-C in heterozygous and homozygous FH patients, making it a potential option for this elusive and refractory disease.
The Mechanism of Lodelcizumab Action
Lodelcizumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody that works to inhibit PCSK9. Lodelcizumab binds to PCSK9 very strongly, preventing PCSK9 from binding to LDLRs. This blockade allows the LDLRs to be recycled back to the surface of the liver, which improves the removal of LDL-C from the bloodstream.
Specific Binding to PCSK9
Lodelcizumab is exceptionally specific for PCSK9 and its extracellular region. Crystallographic studies also revealed that lodelcizumab associates with the catalytic domain of PCSK9, the key to LDLR interaction. This exact binding blocks PCSK9 from playing a role in LDLR degradation and reinstates the receptor's recycling and elimination of LDL-C.
Enhancing LDL-C Clearance
Clinical trials and preclinical work have shown that lodelcizumab has an LDL-C reduction of as much as 60% in hypercholesterolemic patients on its own or in combination with statins. This dramatic reduction is due to the increased availability of LDLRs on hepatocyte surfaces that allows for better uptake and removal of LDL-C.
Extended Half-Life for Sustained Efficacy
Lodelcizumab has a longer half-life and can be administered subcutaneously every two to four weeks. Not only does this dosing schedule facilitate better patient compliance, but it also ensures that PCSK9 activity is permanently suppressed and low LDL-C is maintained over long timeframes.
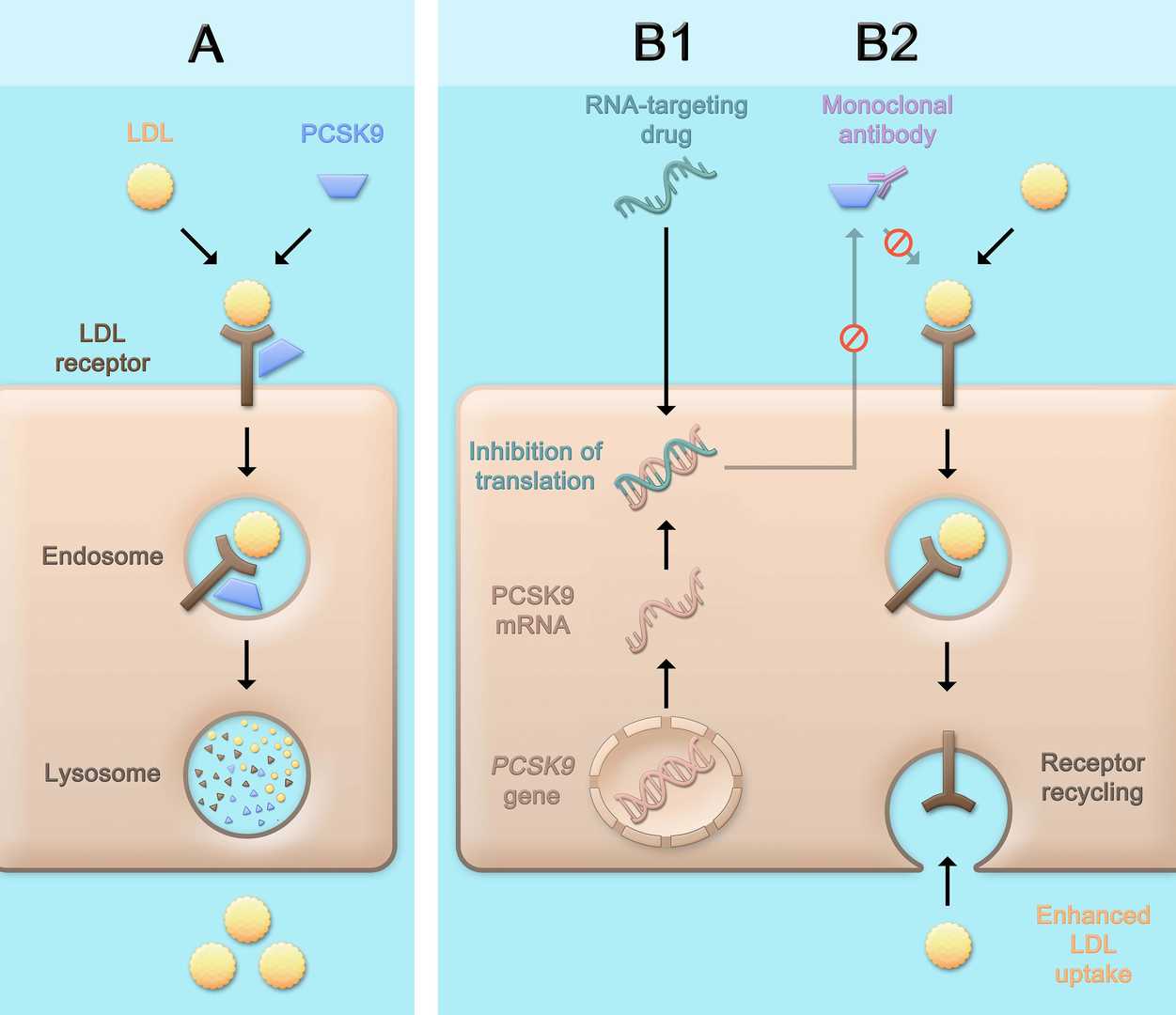 Figure 2. Physiological Role of PCSK9 and Consequences of Therapeutic PCSK9 Inhibition3.
Figure 2. Physiological Role of PCSK9 and Consequences of Therapeutic PCSK9 Inhibition3.
The Clinical Applications of Lodelcizumab
- Family History of Hypercholesterolemia (FH): In heterozygous FH patients, lodelcizumab significantly decreases LDL-C, even in patients who do not respond to standard treatment.
- Statin-Intolerant Patients: Lodelcizumab is a good alternative for those who are resistant to statins because of muscle side effects.
- Patients in High Cardiovascular Risk Groups: In patients with a history of myocardial infarction or cardiovascular events, lodelcizumab decreases LDL-C levels and potentially reduces the risk of future events.
Clinical Projects of Lodelcizumab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT01979601 | Safety, Tolerability, PK and PD of LGT209 in Healthy Volunteers and Patients With Hypercholesterolemia | COMPLETED | Hypercholesterolemia | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | 2010/12/1 |
| NCT01859455 | Safety, Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of LGT209 in Healthy Volunteers With Elevated Cholesterol and in Hypercholesterolemic Patients Treated With Statins | COMPLETED | Hypercholesterolemia|LDL Cholesterol | Novartis Pharmaceuticals | 2011/7/1 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=LGT209
What We Provide
Anti-PCSK9 Recombinant Antibody (Lodelcizumab)
We provide high-quality lodelcizumab for use in ELISA, FC, IP, FuncS, IF, Neut, ICC and most other immunological methods. The product is for lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Derivation
- Humanized (from mouse)
- Type
- IgG1 - kappa
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in ELISA, FC, IP, FuncS, IF, Neut, ICC and most other immunological methods.
- Generic Name
- lodelcizumab
- Related Disease
- Hypercholesterolemia
- UniProt Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/Q8NBP7/entry)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0] without modification.
- Katzmann, Julius L., Ioanna Gouni-Berthold, and Ulrich Laufs. "PCSK9 inhibition: insights from clinical trials and future prospects." Frontiers in Physiology 11 (2020): 595819.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

