Pagibaximab Overview
Introduction of Pagibaximab
Pagibaximab (previously known as BSYX-A110) is a humanized mouse chimeric monoclonal antibody directed against S. epidermidis lipoteichoic acid (LTA), a major cell wall component of gram-positive bacteria. This drug was developed for the prevention of staphylococcal sepsis in infants with low birth weight with being developed for clinical use. This antibody has been shown to: be effective against >90 % CONS clinical strains; detected at a level as low <2 pg/ml; result in >90 % bacterial killing at levels < 10~tg/ml; be effective in preventing infection in several animal models. It has also been shown to be effective in vitro and in animal models in preventing S. aureus infection. In a phase I/II double-blind placebo-controlled trial in very low birth weight (VLBW) infants, pagibaximab exhibited a safety profile that supports continued development with no adverse event attributed to the antibody. Although pagibaximab is not fully human, there was no evidence of anti-drug antibody responses (ADA) and pagibaximab exhibited a serum half- life of 20.5 days which is typical for a human IgG. The long half-life of a mAb is valuable in the prevention of infections during the hospitalization typical for premature infants. On 9 June 2010, orphan designation was granted by the European Commission for pagibaximab for the prevention of sepsis caused by Gram-positive pathogens in premature infants less than or equal to 34 weeks of gestational age.
Mechanism of Action of Pagibaximab
Very-low-birth-weight (VLBW) neonates are at high risk for late-onset hospital-acquired sepsis. Staphylococci, including coagulase-negative staphylococci (CONS) and Staphylococcus aureus, are responsible for between 56 and >75% of hospital-acquired, late-onset neonatal sepsis. Recent reports show continuing increases in resistance of staphylococci to antimicrobial agents. Frequent and prolonged exposures to antimicrobials have been demonstrated to increase the risk of developing infections with resistant organisms. Liptoteichoic acid (LTA) is a cell surface glycolipid present on the surface of Gram-positive bacteria which is thought to share some of the pathophysiological properties of LPS. LTA is proinflammatory and believed to play a role in the development of G rampositive septic shock and other immune sequelae subsequent to bacterial infection. A humanized mouse chimeric IgG1, pagibaximab, specific for staphylococcal LTA is presently under evaluation in a phase II clinical trial for the prevention of staphylococcal sepsis in premature infants. The primary role of pagibaximab in vivo is to promote opsonophagocytic killing, ultimately leading to bacterial clearance. Pagibaximab may also alleviate the symptoms of Gram-positive septic shock by neutralizing staphylococcal LTA. This antibody has been demonstrated to bind and promote killing of S.epidermidis and S.aureus by neutrophils in an in vitro opsonophagocytic assay.
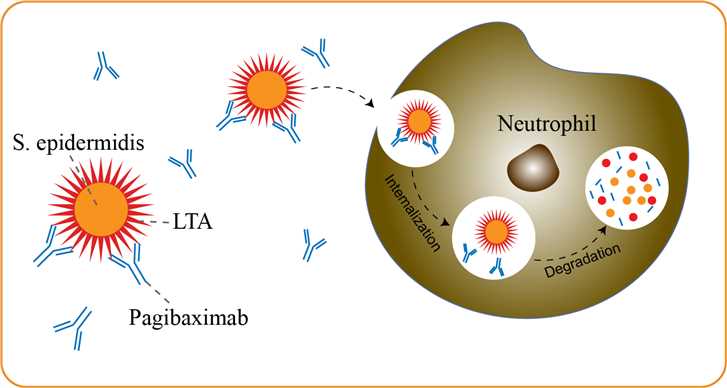
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Pagibaximab
What We Provide
Therapeutic Antibody
Pagibaximab
We provide high-quality Pagibaximab for use in WB, FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF and most other immunological methods. For lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic or any in vivo human use.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


