Selicrelumab Overview
Introduction of Selicrelumab
Selicrelumab, also known as RO7009789 or CP-870,893, is a human immunoglobulin G2 (IgG2) monoclonal antibody agonist of the cell surface receptor CD40 with potential immunostimulatory and antineoplastic activities. This antibody recognizes and binds to the CD40 molecule, a protein prominently expressed on the surface of certain immune cells as well as tumor cells. As a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, CD40 is crucial for B-cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation, as well as for macrophage activation.
Biological and Chemical Properties of Human TNR5 (CD40 Molecule)
Protein Structure
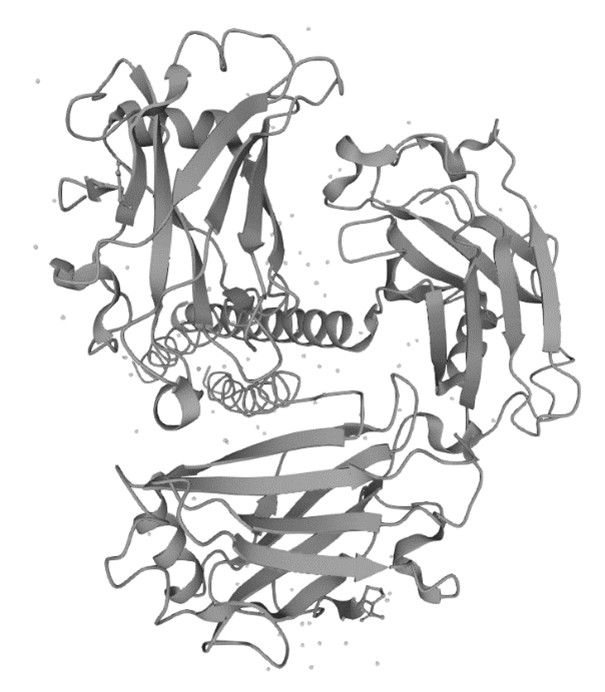 Figure 1. The Structure of Human TNR5 (UniProt)1,2
Figure 1. The Structure of Human TNR5 (UniProt)1,2
The Mechanism of Action of Selicrelumab
CD40, a 48 kDa glycoprotein, belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. It is predominantly expressed on B lymphocytes, professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs) such as dendritic cells and macrophages, fibroblasts, and endothelial cells. The endogenous ligand for CD40 is CD40L (CD154), which is expressed on activated T cells, basophils, and mast cells. Under normal physiological conditions, CD40 signaling facilitates immune homeostasis by enabling effective immune responses against pathogens. However, in pathologic states such as cancer, the role of CD40 becomes more complex. CD40 is often overexpressed in various malignancies such as non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and certain solid tumors, making it an ideal target for cancer treatment. Moreover, these tumor cells can exploit CD40-dependent signaling to evade immune surveillance or promote an immunosuppressive microenvironment. Considering its mixed role in diseased conditions, targeting CD40 in these contexts offers a therapeutic strategy to re-engage the immune system against cancer.
Selicrelumab is a monoclonal antibody agonist of the cell surface receptor CD40. Upon administration, selicrelumab specifically targets and binds to CD40 located on numerous immune cell types. This induces CD40-dependent signaling pathways like those involving NF-κB and JNK and then triggers the proliferation and activation of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), and activates B-cells and T-cells, resulting in an enhanced anti-tumor immune response. The detailed mechanisms can be concretely classified as the direct type and the indirect counterpart according to the interaction with CD40 present on different cells. In terms of its direct mechanism, selicrelumab binds directly to CD40 highly expressed on tumor cells, leading to apoptotic cell death through downstream signaling cascades involving NF-κB and JNK and engagement of natural killer (NK) cells responsible for cell lysis. While selicrelumab also targets CD40 on dendritic cells and macrophages to induce their activation, upregulating the expression of co-stimulatory and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules as well as enhancing antigen presentation and T cell priming. By activating APCs and promoting a more effective antigen presentation, selicrelumab indirectly boosts the cytotoxic activity of CD8+ T cells against tumor cells.
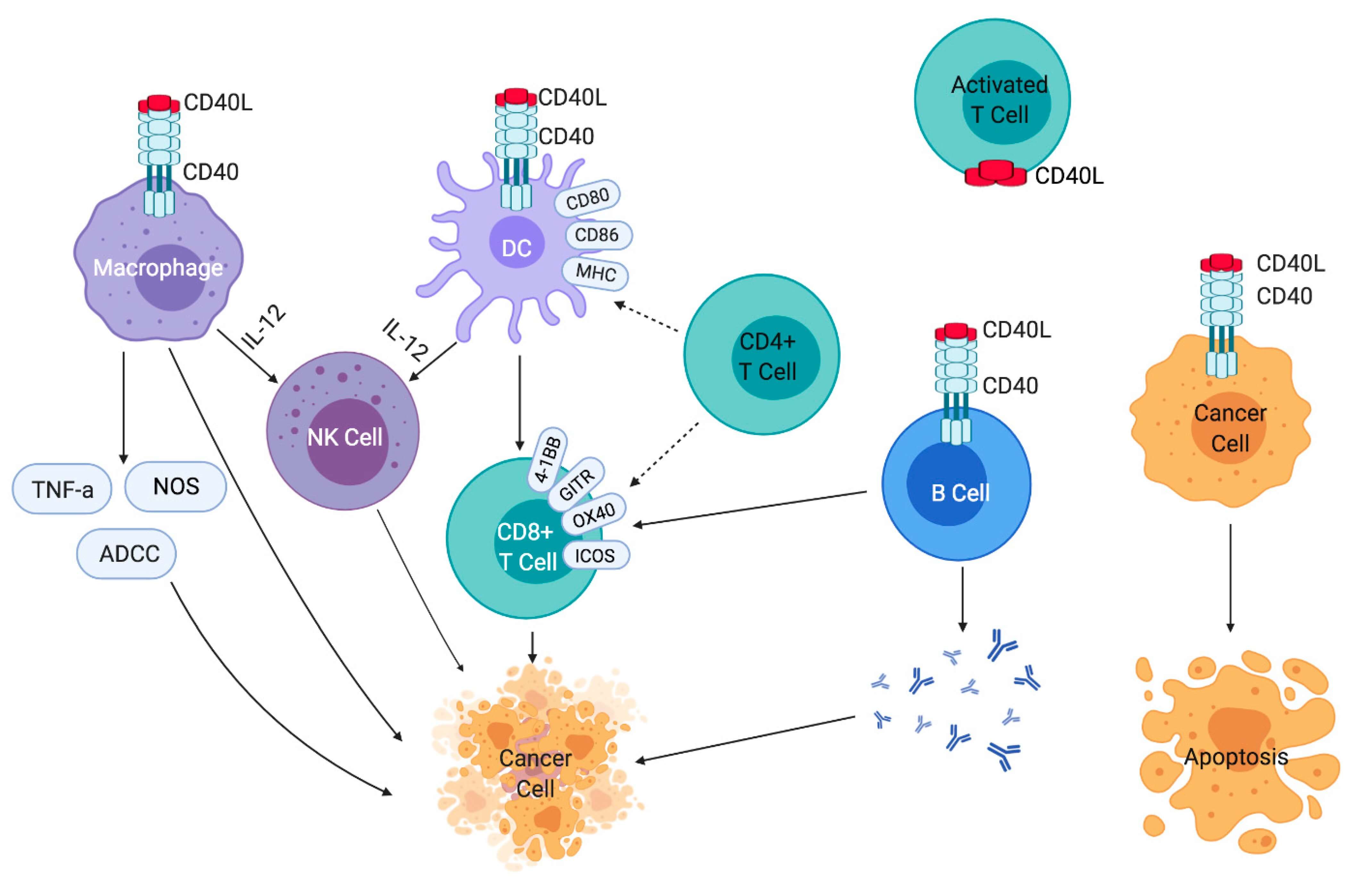 Figure 2. Effects of CD40-CD40L Signaling on Immune Cells and Cancer Cells3,4
Figure 2. Effects of CD40-CD40L Signaling on Immune Cells and Cancer Cells3,4
Clinical Projects of Selicrelumab*
- Combination Therapies: Selicrelumab has been evaluated in combination with other immunotherapies, such as checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-1/PD-L1, to augment anti-tumor responses. This combined approach can potentially overcome resistance mechanisms and improve clinical outcomes.
- Monotherapy: In certain malignancies with high CD40 expression, selicrelumab as a monotherapy has shown efficacy in reducing tumor burden and prolonging survival in preclinical models.
- Vaccination Strategies: By boosting antigen presentation, selicrelumab can enhance the efficacy of cancer vaccines, leading to more robust and long-lasting immune responses.
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT02304393 | A Study of Selicrelumab (RO7009789) in Combination With Atezolizumab in Participants With Locally Advanced and/or Metastatic Solid Tumors | COMPLETED | Solid Tumors | Hoffmann-La Roche | 2014-12-12 |
| NCT02665416 | Study Evaluating the Safety, Pharmacokinetics (PK), Pharmacodynamics (PD), and Therapeutic Activity of Selicrelumab (RO7009789) With Vanucizumab or Bevacizumab in Participants With Metastatic Solid Tumors | COMPLETED | Advanced/Metastatic Solid Tumors | Hoffmann-La Roche | 2016-01-25 |
* The table is excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=Selicrelumab
What We Provide
Anti-Human CD40 Recombinant Antibody (Selicrelumab)
We offer high-quality selicrelumab for usage in ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, and FuncS. The product is intended for laboratory research only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or in vivo human usage.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Human
- Derivation
- Human
- Type
- IgG2, κ
- Specificity
- Human CD40
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, FuncS
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
- CAS
- 1622140-49-1
- Generic Name
- Selicrelumab
- UNII
- 0O39RGI33V
- Related Disease
- Solid tumors
- Uniprot Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P25942/entry#function)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0]. It was not modified and the title was " The Structure of Human TNR5".
- Djureinovic, Dijana et al. "Agonistic CD40 Antibodies in Cancer Treatment." Cancers vol. 13,6 1302. 15 Mar. 2021.
- Images retrieved from Figure 1 "Agonistic CD40 Antibodies in Cancer Treatment." Djureinovic, Dijana, 2021, used under [CC BY 4.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). The image and title were not modified.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

