Emapalumab Overview
Introduction of Emapalumab
Emapalumab (also known as NI-0501), is a fully human monoclonal antibody as a potent inhibitor of neutralizes interferon gamma (IFNγ). It is under investigation as a treatment for primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, a hyperinflammatory condition. On November 20, 2018, the Food and Drug Administration approved this drug for adult and pediatric (newborn and older) patients with primary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) with refractory, recurrent or progressive disease or intolerance with conventional HLH therapy.
Mechanism of Action of Emapalumab
Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a severe immune system disorder, the genetic underpinnings of which are becoming clear. HLH is caused by a severe impairment of cytotoxic T cell function that triggers aberrant activation of the immune system. This is mediated to a large degree by dramatic increase in levels of IFNγ. In preclinical studies, it has demonstrated that neutralizing IFNγ in animal models of HLH reversed organ pathology and normalized key clinical parameters to protect animals from death, whereas inhibition of other cytokines did not provide such protection. Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma or IFNγ) is a cytokine secreted by cells of the immune system to help regulate immune functions. Both the innate and adaptive immune systems use IFN-gamma to fight viral and intracellular bacterial infections. IFNγ is produced by natural killer (NK) and natural killer T (NKT) cells, as well as by CD4± and CD8± Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte (CTL) cells in response to specific pathogens. This particular cytokine is important to the immune system, in part, because it can directly inhibit the ability of viruses to replicate and it helps to both stimulate as well as regulate other immune responses in the body, particularly inflammation. However, abnormal levels of IFNγ are associated with a number of autoinflammatory and autoimmune diseases including lupus, insulin-dependent diabetes, arthritis, and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, among others. Emapalumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody, is a potent inhibitor of IFNγ. It can bind and neutralize IFN-γ, preventing it from inducing pathological effects.
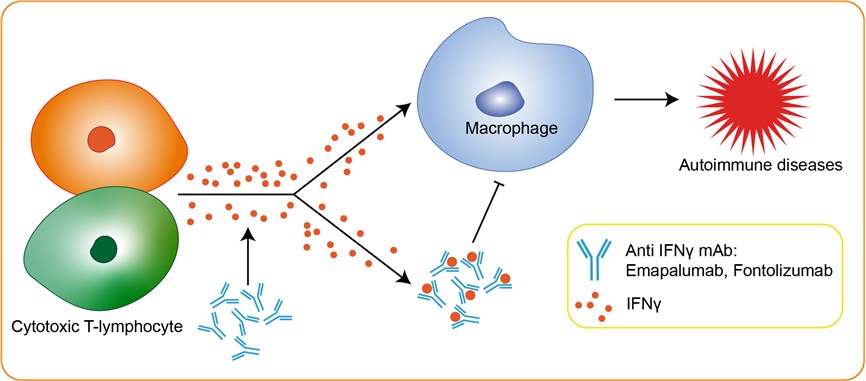 Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Emapalumab
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Emapalumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



