Fresolimumab Overview
Introduction of Fresolimumab
Fresolimumab (GC1008) is a pan-specific, recombinant, fully human monoclonal antibody (mAb) directed against human transforming growth factor (TGF) -β 1, 2 and 3 with potential antineoplastic activity. Fresolimumab was was one of a pair of candidate drugs that were identified for the treatment of the fatal condition scleroderma. It was designed as an IgG4 isotype to minimize immune effector function. Fresolimumab has been used in trials studying the treatment of Primary Brain Tumors, Metastatic Breast Cancer, Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis, Pleural Malignant Mesothelioma, and Primary Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis.
Mechanism of Action of Fresolimumab
TGF-β is a pleiotropic cytokine that is a member of a superfamily of ligands that includes bone morphogenetic proteins and activins. Under normal conditions, TGF-β helps to maintain homeostasis and limit the growth of epithelial, endothelial, neuronal, and hematopoietic cell lineages through anti-proliferative and apoptotic responses. In addition, TGF-β exerts potent effects that influence immune function, differentiation, adhesion, extracellular matrix production, cell motility, angiogenesis, and cytokine production. Early in the transition of premalignant lesions into malignant neoplasms, TGF-β can suppress cell growth; however, in advanced cancers these effects are typically lost. Instead, TGF-β will directly promote tumor growth and metastases. TGF-β-induced cellular changes have been described in many different tumor models and appear to be important for inducing cell migration and promoting metastases. TGFβ also attenuates host antitumor immune responses. With broad activity in natural killer (NK) cells, T cells including T regulatory cells, NKT cells, monocytes/macrophages, and dendritic cells, TGFβ can down-regulate both primary and secondary immune responses and suppress antitumor effector cells. Fresolimumab binds to and inhibits the activity of all isoforms of TGF-β, resulting in the inhibition of tumor cell growth, angiogenesis, and migration, and thereby shows its’ anti-tumor therapeutic efficacy.
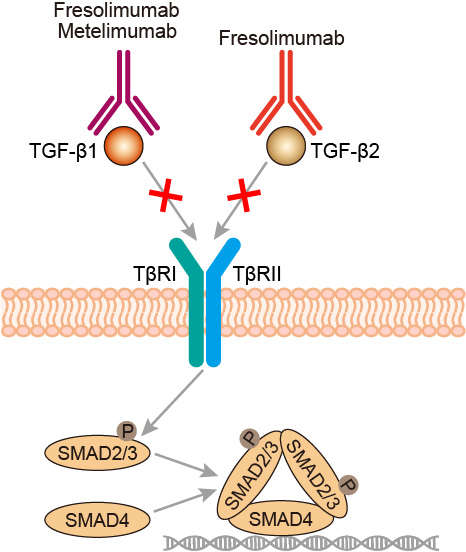 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of fresolimumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of fresolimumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



