Girentuximab Overview
Introduction of Girentuximab
Girentuximab is a chimeric IgG1 monoclonal antibody expressed in CHO which targets to carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX). CAIX is expressed on the surface of most renal cancer cells and is hypothesized to be on the surface of other tumor cells. Its development was suspended as a "naked" or unconjugated antibody during phase III trials due to efficacy. Girentuximab was originally developed by Wilex AG. In addition, it was granted fast track status and orphan drug designation by the FDA for renal cancer. Several phase 2 nonrandomized trials of girentuximab in metastatic RCC demonstrated its safety and tolerability and suggested that it may slow disease progression. The mechanism of antitumor activity of girentuximab is antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), although a contribution by other mechanisms cannot be ruled out.
Mechanism of Action of Girentuximab
While surgical resection is curative in the majority of patients who present with localized renal cell carcinoma (RCC), up to 30% will develop disease recurrence during follow-up, the majority within 5 years. Once the disease progresses to a metastatic state, only high-dose interleukin 2 has been shown to produce durable complete responses, and only in 7% to 10% of patients. Thus, there is interest in developing well-tolerated adjuvant therapies for patients at high risk of recurrence following resection of localized RCC. CAIX is a cell surface glycoprotein member of the carbonic anhydrase family and is expressed in approximately 95% of clear cell RCC (ccRCC) but is absent from normal kidney and minimally expressed in nonrenal tissues and is thus an attractive potential target for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with ccRCC. Interest in CAIX as a potential therapeutic target is supported by the central role that targeted therapies and companion diagnostics have assumed in other malignant neoplasms. Girentuximab is a chimeric immunoglobulin G monoclonal antibody that triggers antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). Girentuximab activates natural killer cells by binding to CAIX. Following binding, girentuximab may be internalized by girentuximab antigen-expressing renal carcinoma cells. In addition, Girentuximab may be useful as a carrier for radioisotopes and other antineoplastic therapeutic agents. Girentuximab is intended to be an adjuvant therapy for the treatment of patients with non-metastatic RCC with a clear cell histology. If licensed, girentuximab would offer the first adjuvant treatment option for patients at high risk of relapse of recurrent disease.
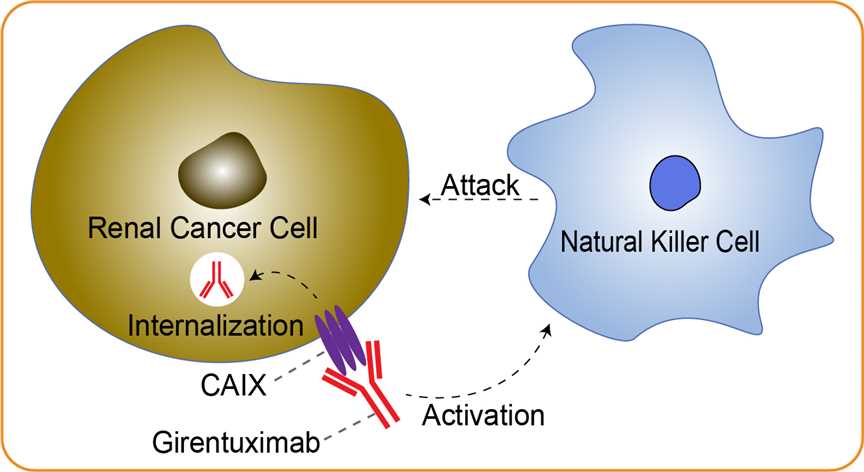
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Girentuximab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



