Imgatuzumab Overview
Introduction of Imgatuzumab
Imgatuzumab (GA201) is a primatized IgG1λ monoclonal antibody (mAb) developed for the treatment of B-cell lymphoma (BCL), colorectal carcinoma (CRC), and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It is a chimeric antibody consisting of human constant and primate (cynomolgus macaque) variable regions. This ‘primatized’ antibody is structurally indistinguishable from human antibodies and, therefore, is not significantly immunogenic in humans. In an open-label, multicenter expansion cohort to evaluate imgatuzumab in pre-treated patients with KRAS-mutant advanced colorectal carcinoma, 25 patients were treated, and the best overall response was stable disease occurring in 40% of patients at 8 weeks, 24% at 16 weeks and 8% (two patients) at 32 weeks. Median overall survival was 9.3 months (95% confidence interval (CI): 5.1–12.3). Treatment-related rash, hypomagnesaemia and infusion-related reactions were the most common adverse events. Comparison of pre- and post-treatment biopsies revealed that the number of tumour-infiltrating immune cells increased notably after one cycle of therapy (median compound immune reactive score of 1491 versus 898 cells/mm3 at baseline), whereas the number of peripheral natural killer cells decreased. A potential association between baseline tumour immune infiltration and clinical efficacy was seen. These data may suggest that the mechanism of action (MoA) of imgatuzumab involves antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)-related immune effects in the tumour and is not limited to simple receptor blockade. In another study, imgatuzumab plus cetuximab leads to a strong downregulation of EGFR and superior cell growth inhibition in vitro without affecting antibody-induced ADCC responses, which support further clinical exploration of the antibody combination in EGFR wild-type NSCLC.
Mechanism of Action of Imgatuzumab
EGFR is a 170 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein composed of a single polypeptide chain. It belongs to the ErbB receptor family, also known as the EGF receptor family. The binding of EGF at the cell surface induces the dimerization of EGFR, which results in the activation of EGFR tyrosine kinase activity and receptor trans-autophosphorylation. Sites of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the activated EGFR interact with downstream signaling proteins to form large signaling complexes. The receptor-signaling protein complexes then initiate the activation of various signaling pathways, which include the KRAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK pathway, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), phospholipase C gamma protein pathway, the anti-apoptotic AKT kinase pathway and the STAT signaling pathway, which leads to cell proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, survival, and adhesion. These cellular processes are often deregulated in malignant cells due to the several mutations harbored in various genes involved in these pathways. Imgatuzumab targets EGFR and works via several anti-tumor mechanisms of action: a strong antibody dependent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), proliferation inhibition via receptor blockage and induction of apoptosis.
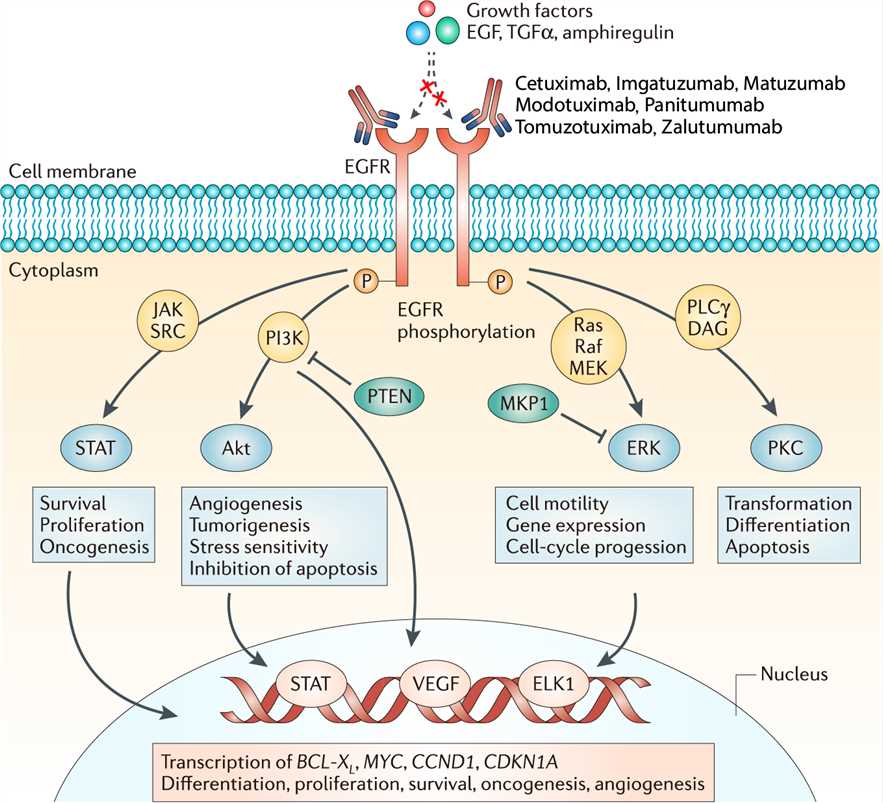
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Imgatuzumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

