Itolizumab Overview
Introduction of Itolizumab
Itolizumab, a novel biological agent, is a 'first in class' humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody. It selectively targets CD6, a pan T cell marker involved in co-stimulation, adhesion and maturation of T cells. It selectively targets CD6, a pan T cell marker involved in co-stimulation, adhesion and maturation of T cells. Itolizumab, by binding to CD6, down regulates T cell activation, causes reduction in synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines and possibly plays an important role by reducing T cell infiltration at sites of inflammation. The results from a study focusing on the immunological and histological effects of itolizumab on psoriasis suggested that itolizumab reduced T-cell proliferation capacity and decreased number of IFN-γ-secreting T-cells. A double blind, placebo controlled, phase III treat –Plaq study of itolizumab successfully met the pre-specified primary end-point of significant improvement in PASI-75 (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index) score after 12 weeks of treatment in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis compared to placebo. In another case report from India, the patient was followed up for more than 4 years after stopping itolizumab and showed sustained response. Itolizumab is being studied in autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, Sjogren's syndrome, and multiple sclerosis. Further, it is being explored for the treatment of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It is also approved in Cuba for the treatment of psoriasis.
Mechanism of Action of Itolizumab
Psoriasis is a common, chronic, immune mediated, inflammatory disease of skin characterized by red patches enclosed with white scales and affects 2-3% of people in the world. CD6 is a surface glycoprotein found on mature T-cells, immature B-cells, the B1a subset of B-lymphocytes, and certain regions of the brain. It plays a pivotal role in cell proliferation, adhesion, differentiation, and survival. Its extracellular region is composed of three SRCR domains. The ligand of CD6, known as CD166 or activated leukocyte cell adhesion molecule (ALCAM), is expressed on T- and B-lymphocytes, APCs, thymocytes, spleen, lymph nodes, and skin and neuronal cells. The CD6 – ALCAM interaction facilitates stable adhesion between T-cells and APCs leading to T-cell differentiation, proliferation, and maturation. The binding site for ALCAM is the third, membrane-proximal domain (SRCR3) of CD6. Itolizumab, however, recognizes SRCR1. Itolizumab is an anti-CD6 monoclonal antibody. CD6 is a costimulatory molecule required for optimal T-cell stimulation by the antigen-presenting cells (APCs). This step is crucial in T-cell proliferation to form Th1 and Th17 cells, which play a major role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. The CD6 pathway contributes to Th1 activation and differentiation of T-cells, promoting a proinflammatory response. Itolizumab, thus, downregulates the gene transcription of proinflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules. This leads to decreased levels of interferon-γ (IFN-γ), interleukin (IL)-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), leading to reduction in the T-cell infiltration at the sites of inflammation. these immunomodulatory effects are not produced by inhibiting ligand binding and inducing T-cell depletion. They result from turning receptor binding nonproductive either by inhibiting new receptor formation or by stimulating the loss of existing receptors or by causing a blockage followed by internalization or downregulation of the receptors. In vitro experiments have shown that itolizumab does not inhibit ALCAM binding to T-cells and does not cause T-cell depletion. However, it is found to inhibit T-cell proliferation induced in the presence of ALCAM and excess IL-2 and downregulates the phosphorylation of intracellular proteins implicated in the CD6-mediated activation pathways and reduces IFN-γ, IL-6, and TNF-α production. Itolizumab, thus, downregulates the inflammatory cascade in a unique manner.
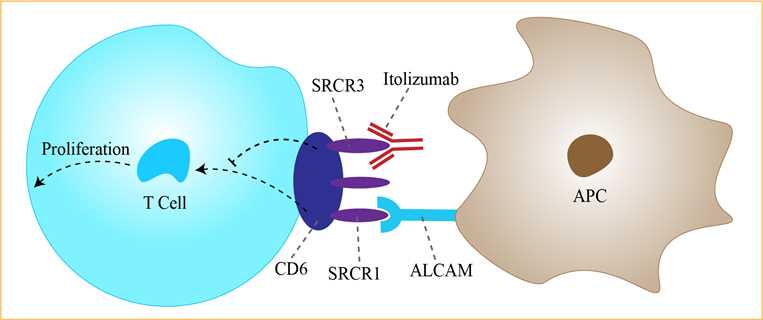
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Itolizumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

