Satralizumab Overview
Introduction of Satralizumab
Satralizumab (SA237), a humanized IgG2 targeting interleukin-6 (IL-6) receptor (IL-6R). The constant and variable regions of the mAb were engineered for half-life extension. It is used to treat neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), an autoimmune disease that affects the optic nerves and spinal cord.
Mechanism of Action of Satralizumab
NMO is an inflammatory disorder of the central nervous system that predominantly affects the optic nerves and spinal cord. NMO is characterized by anti-aquaporin 4 (AQP4) antibody-mediated astrocytopathy. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytokine analyses have shown the significant upregulation of Th2-related cytokines and Th17‐related cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-8 and the granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF), in the active phase of NMO patients. Among these significantly elevated cytokines, IL-6 presumably plays an important role in the immunopathogenesis of NMO, because it is involved in the production of anti-AQP4 antibody in the peripheral circulation and in the enhancement of inflammation in the central nervous system, the level of IL-6 in CSF can be a biomarker of the prognosis and disease activity of NMO. Satralizumab targets the IL-6 receptor, thereby inhibiting the IL-6-involved pathways which participate in the pathogenesis of NMO.
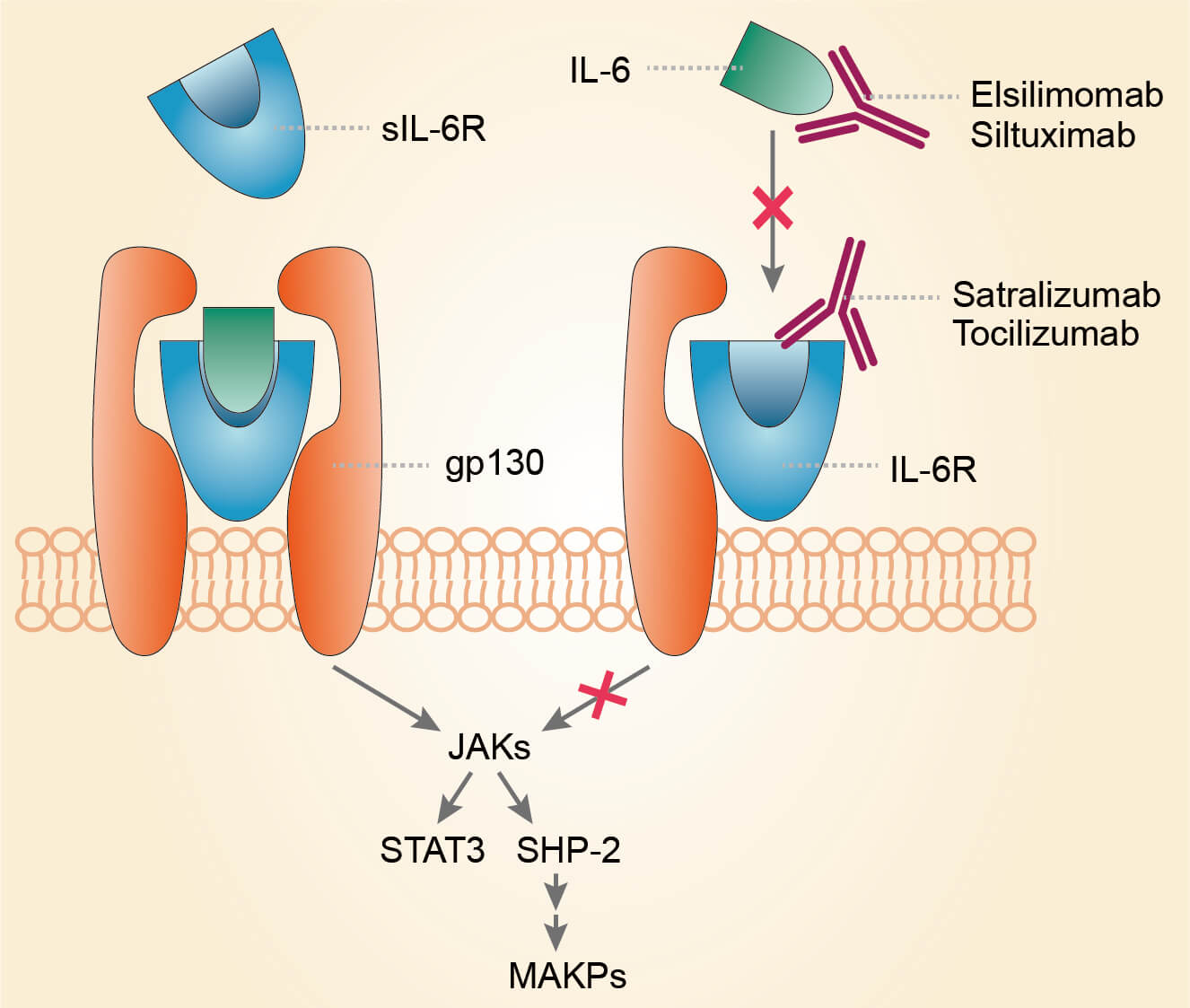 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of satralizumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of satralizumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

