Teplizumab Overview
Introduction of Teplizumab
Simtuzumab (formerly GS-6624) is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that specifically binds and inhibits lysyl oxidase homolog 2 (LOXL2) and acts as an immunomodulator. Simtuzumab binds to LOXL2, was shown to have a role in suppressing bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in a murine model. Therefore, simtuzumab was a logical choice as a potentially effective pharmacological treatment for treatment of IPF.
Know more about type I diabetes.
Biological and Chemical Properties of Teplizumab
Protein Structure
 Figure 1 Structure of Teplizumab
Figure 1 Structure of Teplizumab
Protein Chemical Formula
C6462H9938N1738O2022S46
Protein Average Weight
150000.0 Da (approximate)
Mechanism of Action of Teplizumab
Teplizumab is an anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody specifically designed to target and modulate T cells, which play a crucial role in the immune response. The CD3 complex is a key component of the T cell receptor (TCR) that transmits activation signals upon recognizing antigens. In autoimmune diseases like type 1 diabetes (T1D), T cells mistakenly attack the body's own tissues, such as the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. By binding to the CD3 epsilon chain, teplizumab interferes with T cell activation and reduces the immune system's attack on these cells.
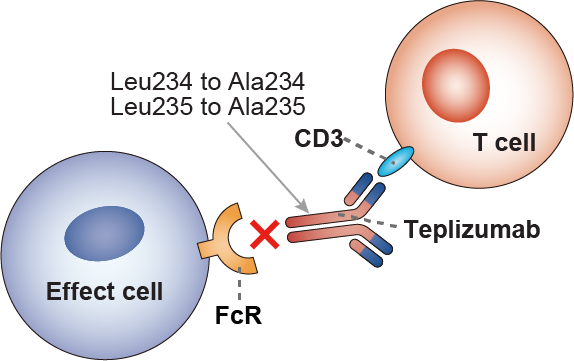 Figure 2 Mechanism of action of Teplizumab
Figure 2 Mechanism of action of Teplizumab
Teplizumab works through several mechanisms to achieve this modulation. It induces a state of partial inactivation in T cells, reducing their aggressive autoimmune response while preserving their ability to fight infections. Additionally, teplizumab promotes the development and function of regulatory T cells (Tregs), which help maintain immune tolerance by suppressing overactive immune responses. The drug also modulates effector T cells, decreasing their production of inflammatory cytokines and altering their trafficking patterns to reduce their infiltration into the pancreas. This multi-faceted approach helps to preserve the function of pancreatic beta cells, delaying the progression of T1D and maintaining endogenous insulin production for a longer period.
Targeting the CD3 Complex
The CD3 complex is an integral part of the T cell receptor (TCR) complex, which is crucial for T cell activation. This complex is made up of several protein chains that work together to transduce activation signals from the T cell surface to its interior. When T cells recognize antigens presented by the body's own cells, the CD3 complex plays a key role in initiating the immune response. In autoimmune diseases like T1D, this response becomes misdirected against the body's own tissues. Teplizumab's ability to bind specifically to the CD3 epsilon chain disrupts this signaling process, leading to a reduction in T cell activation and proliferation.
Inducing Partial Inactivation of T Cells
Teplizumab does not completely deactivate T cells; instead, it induces a state of partial inactivation. This means that T cells are still functional but less likely to launch a full-scale autoimmune attack. This partial inactivation is beneficial because it reduces the harmful immune response against pancreatic beta cells while preserving the immune system's ability to respond to infections. By striking this balance, teplizumab helps to maintain immune function without exacerbating autoimmune activity.
Promoting Regulatory T Cells (Tregs)
Regulatory T cells (Tregs) play a crucial role in maintaining immune tolerance by suppressing overactive immune responses. Teplizumab has been shown to increase the number and activity of Tregs, thereby promoting a more balanced immune environment. Tregs help to prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own tissues, which is particularly important in autoimmune diseases like T1D. By enhancing the function of Tregs, teplizumab contributes to the preservation of pancreatic beta cells and the delay in disease progression.
Modulating Effector T Cells
Effector T cells are responsible for carrying out immune attacks, including those against the body's own tissues in autoimmune diseases. Teplizumab modulates the activity of effector T cells by reducing their production of inflammatory cytokines, which are signaling molecules that promote inflammation and tissue destruction. By decreasing the levels of these cytokines, teplizumab helps to mitigate the damage caused by the immune system to pancreatic beta cells. This modulation of effector T cells is a key mechanism by which teplizumab protects beta cell function.
Altering T Cell Trafficking
Teplizumab also affects the movement and localization of T cells within the body. By altering the expression of certain surface molecules on T cells, teplizumab reduces their ability to migrate into the pancreas. This limits the infiltration of autoreactive T cells into the pancreatic islets, where beta cells reside. By preventing these cells from reaching and attacking the beta cells, teplizumab further helps to preserve insulin production and delay the onset of T1D.
Fc Receptor Non-Binding
A critical feature of teplizumab is its Fc receptor non-binding modification. Fc receptors are found on various immune cells and bind to the Fc region of antibodies, leading to different immune responses, such as antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) or phagocytosis. By engineering teplizumab to be Fc receptor non-binding, researchers have minimized the risk of these unwanted immune responses. This modification reduces the likelihood of broad immune activation and potential adverse effects, enhancing the safety profile of teplizumab. The Fc receptor non-binding characteristic ensures that teplizumab specifically targets T cells without triggering additional immune system activation that could exacerbate autoimmune conditions or lead to other complications.
Long-Term Immune Modulation
The effects of teplizumab extend beyond the immediate modulation of T cell activity. Studies have shown that a short course of teplizumab can lead to lasting changes in the immune system. These long-term effects are thought to result from the induction of immune tolerance and the establishment of a more regulatory immune environment. The drug's ability to promote long-term immune regulation and balance is a significant factor in its efficacy for delaying the onset of T1D.
High Throughput Antibody Production
Creative Biolabs offers comprehensive suite of high throughput antibody production services for both therapeutic monoclonal antibodies and reagent antibodies.
Glycosylation Analysis of Therapeutic Glycoproteins
We recently provide an update series of services and related products in glycan analysis for determining unique glycan features, including assessment of glycosylation site, glycan structure, and carbohydrate content.
Non-GMP Antibody Production
Creative Biolabs possesses extensive expertise in transitioning monoclonal antibodies through the whole product life cycle from concept in early-stage development to large-scale non-GMP commercialization.
rAb Production in Cell-Free System
Creative Biolabs is offering the most comprehensive services for antibody production. We established cell-free protein expression platform to support the development of antibodies and other therapeutics.
Artificial Intelligence-Driven Antibody Discovery Services
Creative Biolabs employs an AI-driven platform for high-throughput recombinant antibody expression and antibody affinity maturation to facilitate rapid and efficient screening. The antibody affinity can be increased by >102 times. Currently, Creative Biolabs can offer seamless solutions for antibody development, encompassing antigen design and preparation, animal immunization, and harvesting.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

