Timolumab Overview
Introduction of Timolumab
Timolumab, as known as BTT1023, is a fully human, monoclonal, anti-AOC3 antibody which blocks the adhesion function of AOC3, thereby diminishing leucocyte entry into sites of tissue inflammation. This drug was developed for the treatment of Psoriasis, Rheumatoid arthritis, and Primary sclerosing cholangitis. BTT1023 appears to be safe and well tolerated in humans: BTT1023 has been given in doses up to 8 mg/kg in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis after oral premedication (cetirizine and ibuprofen) and also appears safe and well tolerated in repeated intravenous dosing. Timolumab is being evaluated in Phase II clinical trial NCT02239211, for its potential to treat patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis, an uncommon and progressive disease of the bile ducts characterized by inflammation and obliterative fibrosis. Phase I studies for RA and psoriasis have been completed.
Mechanism of Action of Timolumab
Amine oxidase, copper containing 3 (AOC3), also known as vascular adhesion protein (VAP-1) and HPAO, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the AOC3 gene on chromosome17. VAP-1 is primarily localized on the cell surface on the adipocyte plasma membrane. However, circulating VAP-1 has been shown to be the main source of SSAO in human serum. VAP-1 has adhesive properties, functional monoamine oxidase activity, and possibly plays a role in glucose handling, leukocyte trafficking, and migration during inflammation. This rise in metabolic products contributes to generating advanced glycation end-products and oxidative stress along with the monoamine detoxification in the organism. VAP-1 is found in the smooth muscle of blood vessels and various other tissues, and can mostly be found in two forms: tissue-bound and soluble isoforms. The tissue-bound SSAO is primarily located in the leukocytes, adipocytes, and the endothelium of highly vascularized tissues, including the kidney, liver, and gonads. The soluble form, which is commonly known as VAP-1, is a proinflammatory protein derived from shedding of the transmembrane protein. It is highly expressed on the endothelium of the lung and trachea, and absent from leukocytes and epithelial cells. It moderates leukocyte recruitment, is both an adhesion molecule and a primary amine oxidase, and plays a role in clinical disease. Although the mechanism of action is not fully elucidated, BTT1023 is a fully human monoclonal antibody that targets VAP-1. It could block the adhesion function of VAP-1, thereby diminishing leucocyte entry into sites of tissue inflammation. In vivo, blocking VAP-1 function with an anti-mouse anti-VAP-1 antibody significantly alleviates inflammation in mouse models of arthritis and liver fibrosis.
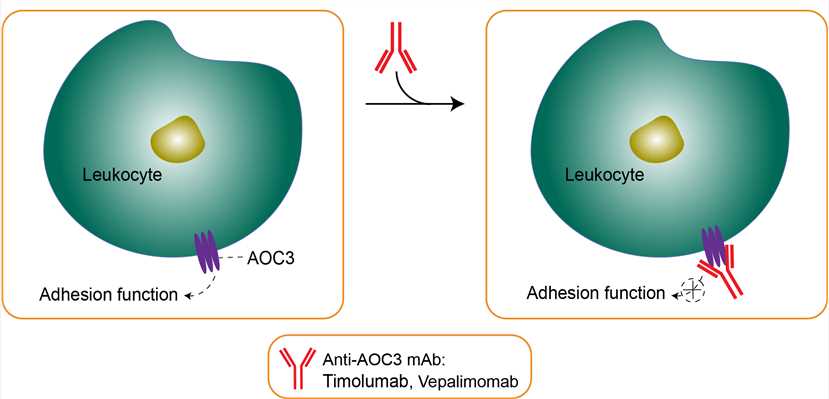
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Timolumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

