Tomuzotuximab Overview
Introduction of Tomuzotuximab
Tomuzotuximab is a novel immune-enhanced monoclonal antibody (mAb) against the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). Tomuzotuximab has a fully human glycosylation pattern and is glyco-optimized at its Fc domain to improve its efficacy and reduce it side effects, while fully retaining the affinity, specificity, EGFR inhibition and induction of apoptosis of cetuximab. Elimination of fucose leads to a mean antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) increase of tomuzotuximab compared with cetuximab of 10-50-fold depending on the Fc receptor variant, while elimination of the α-gal epitope, which can cause severe IgE-mediated hypersensitive reactions to cetuximab, will improve its tolerability. All patients but one had progressive locoregional or metastatic disease and had exhausted available standard treatment procedures. According to a Phase I study in patients with advanced carcinomas, all patients but one had progressive locoregional or metastatic disease and had exhausted available standard treatment procedures. The most frequent reason for study termination was progressive disease (PD) (29 patients, 70.7%), followed by adverse events (AE) and death (5 patients each, 12.2%). One patient did not meet the inclusion criteria, and another continued with tomuzotuximab on a named patient use after the study was closed (4.9%). A phase IIb trial of chemotherapy and weekly tomuzotuximab or cetuximab followed with maintenance therapy with the corresponding mAb in patients with recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is ongoing.
Mechanism of Action of Tomuzotuximab
EGFR is a 170 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein composed of a single polypeptide chain. It belongs to the ErbB receptor family, also known as the EGF receptor family. The binding of EGF at the cell surface induces the dimerization of EGFR, which results in the activation of EGFR tyrosine kinase activity and receptor trans-autophosphorylation. Sites of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the activated EGFR interact with downstream signaling proteins to form large signaling complexes. The receptor-signaling protein complexes then initiate the activation of various signaling pathways, which include the KRAS-BRAF-MEK-ERK pathway, phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), phospholipase C gamma protein pathway, the anti-apoptotic AKT kinase pathway and the STAT signaling pathway, which leads to cell proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, survival, and adhesion. These cellular processes are often deregulated in malignant cells due to the several mutations harbored in various genes involved in these pathways. Tomuzotuximab targets EGFR and works via several anti-tumor mechanisms of action: a strong antibody dependent ADCC, proliferation inhibition via receptor blockage and induction of apoptosis.
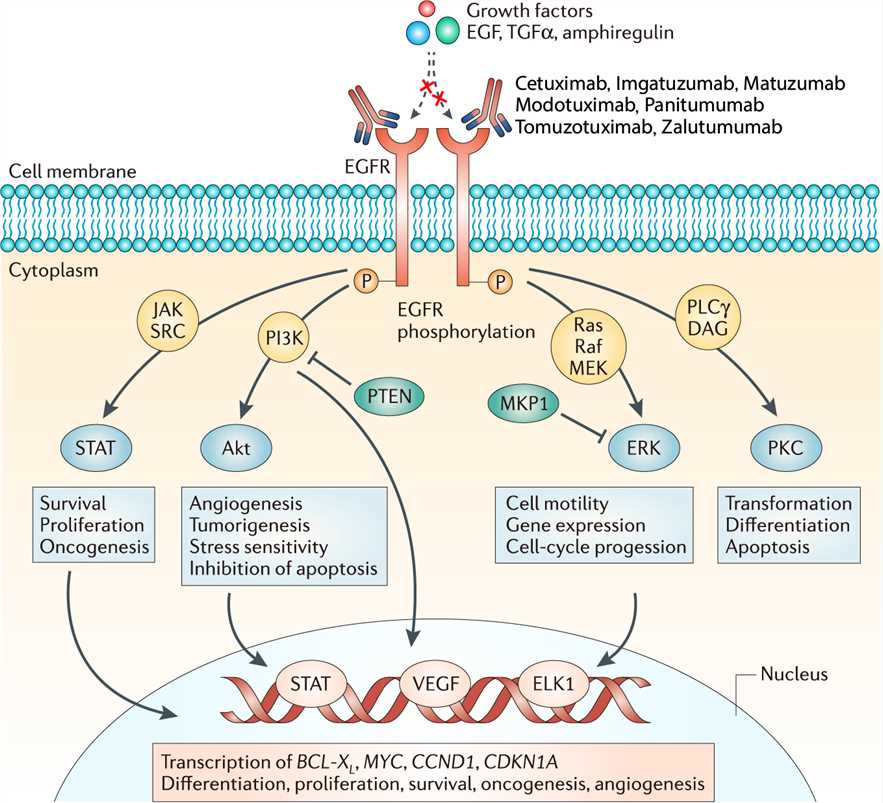
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Tomuzotuximab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



