Afutuzumab Overview
Introduction of Afutuzumab
Afutuzumab is a new type II monoclonal antibody that targets CD20 which is encoded by the MS4A1 gene. It is also referred to as obinutuzumab, GA101, Gazyva, and Gazyvaro. Developed by GlycArt Biotechnology AG and marketed by Roche, afutuzumab is a cancer medication used for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Compared to type I antibodies like rituximab and ofatumumab, which exhibit higher complement-dependent cytotoxicity, afutuzumab may provide more direct cytotoxic effects and enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC). In a large-scale randomized phase III clinical trial, the combination of chlorambucil and afutuzumab, when administered with an improved early loading dose, showed improved response rates and progression-free survival compared to rituximab and chlorambucil, without a statistically significant increase in toxicity. This was observed particularly in older patients with renal impairment and/or serious comorbidities. Afutuzumab expands the list of CLL therapy options by offering a less harmful and more active targeted medication, providing patients and doctors with more treatment choices. It is approved as a second-line treatment for follicular lymphoma and received approval of U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2013 under the trade name Gazyva. In Europe, the European Medicines Agency approved it under the name Gazyvaro for treating chronic lymphocytic leukemia in individuals who had not previously received chemotherapy.
Biological and Chemical Properties of Afutuzumab
Protein Structure
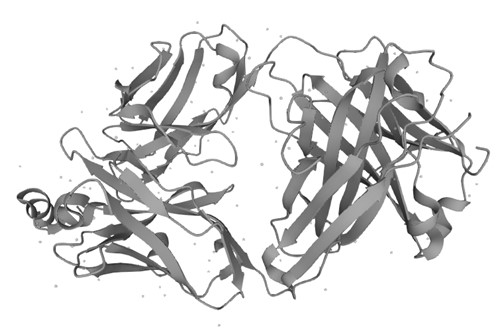 Figure 1. Structure of Human CD20 (UniProt)1,2
Figure 1. Structure of Human CD20 (UniProt)1,2
Protein Chemical Formula
C6512H10060N1712O2020S44
Protein Average Weight
The average weight of the protein is approximately 146100.0 Da.
Mechanism of Afutuzumab Action
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a malignancy that affects a specific type of white blood cell known as lymphocytes. In CLL, these lymphocytes become cancerous and multiply uncontrollable, crowding out healthy cells and impairing the immune system's ability to fight infections. CLL predominantly affects B-lymphocytes, a type of lymphocyte responsible for producing antibodies to help fight infections. The protein CD20 is frequently located on the surface of B-lymphocytes, serving as a marker for this specific type of white blood cell. Therefore, CD20 is a target for therapy in diseases like CLL where abnormal B-lymphocytes accumulate in the body. To combat CLL, targeted therapies have been developed to specifically attack and eliminate the cancerous B-lymphocytes. One such targeted therapy is afutuzumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds to CD20 on the surface of B-lymphocytes. By binding to CD20, afutuzumab triggers the destruction of the cancerous B-lymphocytes through various mechanisms.
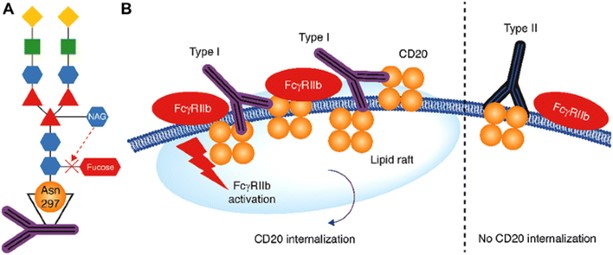 Figure 2. Structure and Proposed Binding Behavior of Afutuzumab3,4
Figure 2. Structure and Proposed Binding Behavior of Afutuzumab3,4
CD20 mAbs are classified into type I and type II based on their capacity to cause the rearrangement of CD20 molecules into lipid rafts upon binding (Figure 2). Type I CD20 mAbs (rituximab, ofatumumab, ocaratuzumab, and ublituximab) cause CD20 molecules to reorganize into lipid rafts, thereby activating the complement system's classical pathway. In contrast, type II CD20 mAbs, such as afutuzumab, have a low complement activation but can directly induce cell death when bound to CD20 without the need for secondary antibodies. The fundamental distinction is whether they can cause CDC (type I) or not (type II). The primary mechanisms of action of anti-CD20 antibodies include:
Antibody-Dependent Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity (ADCC)
One key mechanism is antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC), where immune cells recognize the bound antibody on the cancer cell and destroy it. Afutuzumab binds to CD20 on the surface of B cells, attracting immune cells such as natural killer cells. These immune cells recognize the antibody-coated B cells and release toxic compounds, such as perforin and granzymes, leading to the lysis of the target cells.
Fab-Mediated Direct Induction of Cell Death
In contrast to type I, type II CD20 mAb, such as afutuzumab, are able to induce direct cell death upon binding to CD20 in the targeted cells, which is known as apoptosis. This is independent of the Fc part of the antibody, but it demands F(ab)2 fragments and the interaction of at least two CD20 molecules. The induction of programmed cell death (PCD) follows a mechanism that is independent of BCL-2 and caspases but requires lysosomal enzymes. And this mechanism helps to eliminate the malignant B cells from the body.
FcγR-Mediated Phagocytosis
Afutuzumab, a type II Fc-optimized mAb, has a reduced ability to activate complement but an enhanced ability to recruit FcγRIIIA-expressing cytotoxic and phagocytic effectors and to induce direct cytotoxicity.
Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC)
Some type I anti-CD20 mAbs can also activate the complement system, part of the immune system that helps to clear pathogens and damaged cells. Binding to CD20 on B cells activates the complement system, leading to the formation of the membrane attack complex which causes cell lysis. However, afutuzumab does not activate the complement system to induce cytotoxicity like type I anti-CD20 mAbs.
Induction of long-Term Anti-Tumor Immunity
In addition to direct antitumor effects, CD20 mAb may produce long-term antitumor immunity. Antibody-opsonized tumor cells can be phagocytosed by tissue-resident dendritic cells (DCs), which can stimulate the production of tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Besides, immune complexes (ICs) generated after CD20 mAb treatment are powerful DC activators and may trigger antitumor immunity. DCs absorb ICs via activating FcγRs, resulting in strong activation and cross-presentation of tumor-derived antigens.
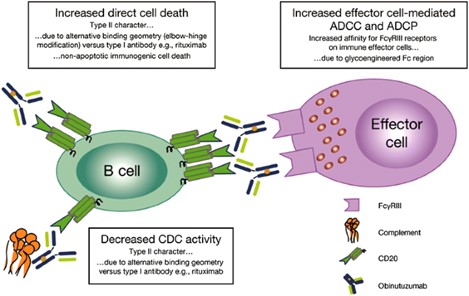 Figure 3. Putative Mechanism of Action of Afutuzumab3,4
Figure 3. Putative Mechanism of Action of Afutuzumab3,4
Afutuzumab is a type II anti-CD20 mAb, differing from most recombinant anti-CD20 mAbs which belong to type I. By activating the first three mechanisms (ADCC, Fab-mediated direct cellular death induction, and FcγR-mediated phagocytosis), afutuzumab targets and destroys CD20-positive B cells. This makes it an effective treatment for diseases such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia and other CD20-positive B-cell malignancies, as well as for inducing long-term anti-tumor immunity.
Clinical Projects of Afutuzumab*
| NCT ID | Study Title | Study Status | Conditions | Sponsor | Start Date |
| NCT03374137 | Observational Study to Monitor the Safety and Effectiveness of Obinutuzumab in Follicular Lymphoma or Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | COMPLETED |
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Follicular Lymphoma |
Hoffmann-La Roche | 2018-03-09 |
| NCT05510219 | Safety Analysis of Intravenous Rapid Infusion of Obinutuzumab in Patients With B-cell Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma in China | RECRUITING |
Obinutuzumab Intravenous Infusion Reaction Rapid Infusion |
The First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University | 2022-01-01 |
| NCT03529227 | Gazyva Infusion Reaction Investigation (GAIRI) | RECRUITING | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia | Healthy Future | 2018-03-31 |
| NCT04560322 | Venetoclax-Obinutuzumab +/- Acalabrutinib in R/R CLL | RECRUITING |
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma |
Massachusetts General Hospital | 2020-10-19 |
* The table was excerpted from the following website: https://clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=Afutuzumab
Approved Drugs of Afutuzumab**
| INN (trade name) | Therapeutic area | Strength | Route | Company | Marketing start | Market |
| GAZYVA | Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) | 1000mg/40mL | Intravenous | GENENTECH | 11/01/2013 |

|
** Information presented in the table was collected from the following website:
https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/scripts/cder/daf/index.cfm?event=BasicSearch.process
What We Provide
Anti-Human CD20 Recombinant Antibody (Afutuzumab)
We provide high-quality afutuzumab for use in IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, ICC and most other immunological methods. For lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic, or any in vivo human use.
- Immunogen
- The details of the immunogen for this antibody are not available.
- Host Species
- Mouse
- Derivation
- Humanized (from mouse)
- Type
- IgG3 - kappa
- Specificity
- Tested positive against native human antigen.
- Species Reactivity
- Human
- Applications
- Suitable for use in IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, ICC and most other immunological methods.
- Trade name
- obinutuzumab, obinutuzumab
- CAS
- 949142-50-1
- Generic Name
- Afutuzumab
- ATC Code
- L01XC15
- UNII
- O43472U9X8
- MW
- 146.1 kDa
- UniProt Database (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprotkb/P11836/entry)
- The image was retrieved from UniProt Database and used under [CC BY 4.0]. It was not modified and the titles was "Structure of Human CD20".
- Tobinai, Kensei et al. "A Review of Obinutuzumab (GA101), a Novel Type II Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody, for the Treatment of Patients with B-Cell Malignancies." Advances in therapy vol. 34,2 (2017): 324-356.
- Images retrieved from Figure 1 and Figure 2 "A Review of Obinutuzumab (GA101), a Novel Type II Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody, for the Treatment of Patients with B-Cell Malignancies." Tobinai, Kensei, 2017, used under [CC BY 4.0] (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). The images were not modified compared to the original figures, and the titles were changed to "Structure and Proposed Binding Behavior of Afutuzumab" and "Putative Mechanism of Action of Afutuzumab" respectively.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

